The Role of Geoinformatics in Predicting Floods
Introduction
Geoinformatics is the science and technology of gathering, processing, and delivering geographic information, or spatially referenced information. It encompasses a broad range of disciplines including geography, computer science, statistics, cartography, geodesy, and others. This field plays a crucial role in predicting floods, a natural disaster that causes significant damage worldwide.
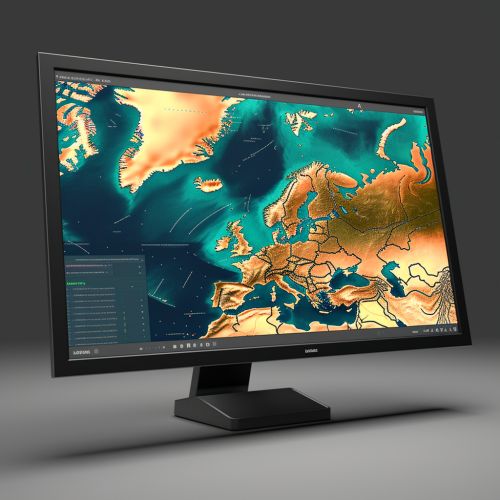

Role of Geoinformatics in Predicting Floods
The primary role of geoinformatics in predicting floods is to provide accurate, timely, and relevant geographic data. This data is used in hydrological models to predict the occurrence, extent, and severity of floods.
Data Collection
Geoinformatics uses various tools and techniques for data collection. These include remote sensing, GPS, and GIS. Remote sensing involves the use of satellites or aircraft to collect data about the earth's surface. This data can include information about land use, vegetation cover, soil type, and topography, all of which are important factors in flood prediction.


Data Processing
Once the data is collected, it is processed using GIS. This involves cleaning the data, integrating different data sources, and transforming the data into a format that can be used in hydrological models. GIS also allows for the visualization of the data, which can aid in understanding the potential flood risk.
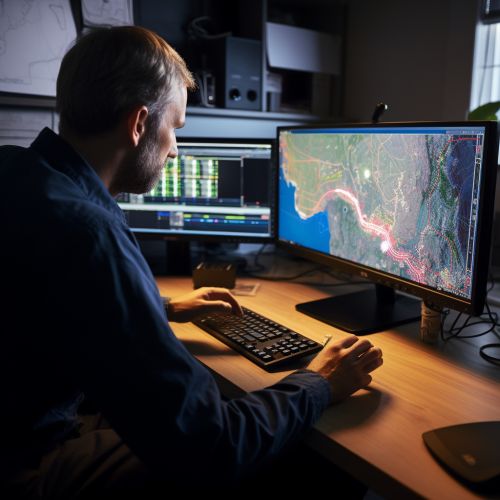


Hydrological Modeling
The processed data is then used in hydrological models to predict floods. These models simulate the movement of water through a catchment area and can predict how much water will flow into a river or stream during a rainfall event. The models can also predict the extent of flooding based on the topography and land use of the area.
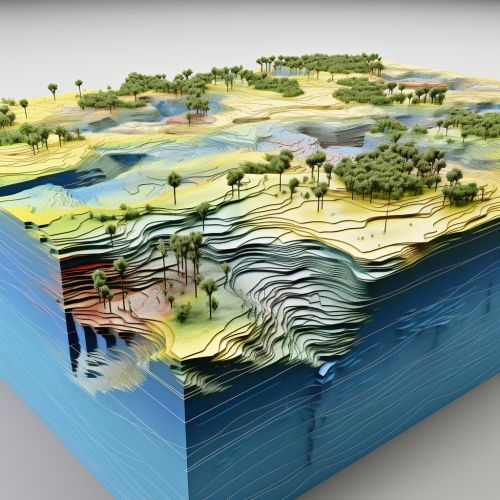

Advantages of Using Geoinformatics in Flood Prediction
Geoinformatics offers several advantages in flood prediction. It allows for the collection of large amounts of data over large areas, which would be difficult and time-consuming to collect manually. The data is also collected in real-time, allowing for timely predictions. Furthermore, the use of GIS allows for the integration of different types of data, leading to more accurate predictions.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its advantages, there are also limitations and challenges in using geoinformatics for flood prediction. These include the accuracy of the data collected, the complexity of the hydrological models, and the need for skilled personnel to operate the systems and interpret the results.
Conclusion
Geoinformatics plays a crucial role in predicting floods. It provides the data needed to understand the risk of flooding and to plan for flood events. Despite some limitations, the use of geoinformatics in flood prediction is likely to increase in the future as the technology continues to advance.