Geodesy
Introduction
Geodesy, also known as geodetics, is a scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth. The field incorporates both the study of Earth's shape and its gravitational field. Geodesy's two primary concerns are the precise determination of positions on Earth and the detailed study of variations in Earth's gravity.


History
The history of geodesy began in ancient times with the Greeks and Romans, who made the first recorded measurements of the Earth. The term "geodesy" comes from the Greek words "ge" meaning Earth and "daiein" meaning to divide or separate. Early geodesists attempted to determine the size and shape of the Earth, with notable contributions from figures such as Eratosthenes and Hipparchus.


Geodetic Measurements and Techniques
Geodesy involves a variety of measurements and techniques. These include terrestrial techniques such as triangulation, trilateration, and leveling, as well as space-based techniques like satellite geodesy and GNSS.
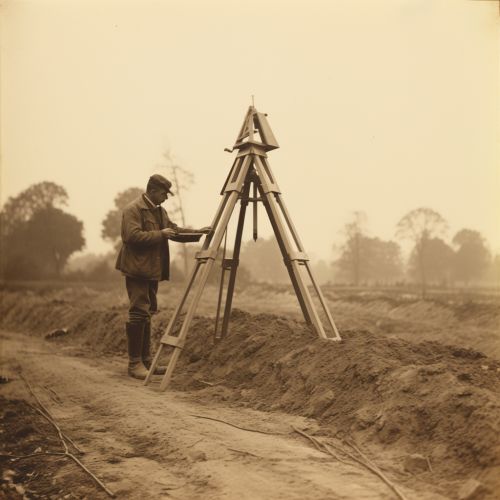
Terrestrial Techniques
Terrestrial techniques involve measurements made on the Earth's surface. Triangulation is a method of determining the location of a point by measuring angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline. Trilateration is similar, but uses the lengths of these lines instead. Leveling involves measuring vertical distances to determine height differences.


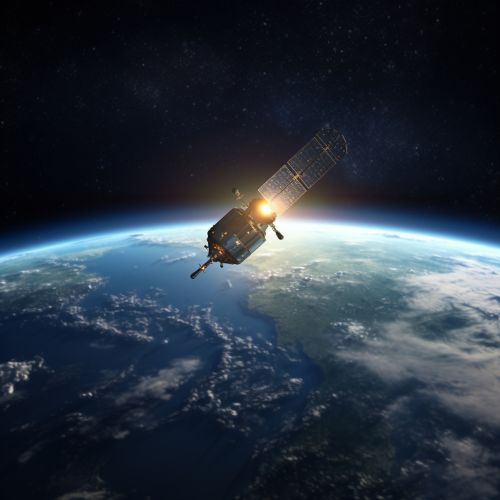
Space-Based Techniques
Space-based techniques involve the use of artificial satellites. Satellite geodesy includes techniques like Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI), Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR), and the use of GNSS such as the Global Positioning System (GPS). These techniques allow for precise measurements of distances and positions on the Earth's surface.


Geodetic Reference Systems
Geodesy uses reference systems to accurately represent the Earth. These include geodetic datums, coordinate systems, and map projections. A geodetic datum is a set of reference points used to locate places on the Earth. Coordinate systems, such as the geographic coordinate system and the Cartesian coordinate system, are used to define positions. Map projections are methods of representing the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map.
Applications of Geodesy
Geodesy has a wide range of applications. It is used in surveying and mapping, in navigation systems like GPS, and in scientific research into Earth's shape, orientation in space, and gravity field. Geodesy also plays a crucial role in geospatial intelligence and Earth observation systems.


