The Role of Geoinformatics in Disaster Risk Reduction
Introduction
Geoinformatics, also known as geospatial informatics, is an interdisciplinary field that utilizes a wide range of technologies to gather, analyze, interpret, distribute, and use geographic information. This field plays a crucial role in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR), a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and reducing the risks of disaster. This article explores the role of geoinformatics in disaster risk reduction, detailing its applications, benefits, and challenges.


Geoinformatics and its Relevance to Disaster Risk Reduction
Geoinformatics combines the science of geography, the technology of information systems, and the methods of informatics to study and manage spatial information. It employs tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing to collect, process, and visualize geographic data. This data is crucial in disaster risk reduction, as it aids in the identification of hazard-prone areas, the assessment of vulnerability, and the planning and implementation of mitigation strategies.


Applications of Geoinformatics in Disaster Risk Reduction
Hazard Identification and Assessment
Geoinformatics plays a crucial role in the identification and assessment of natural hazards such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, and cyclones. Using GIS and remote sensing, scientists can map hazard-prone areas, predict the likelihood of future events, and assess the potential impact of these events. For example, remote sensing can detect changes in land surface that may indicate an increased risk of landslides, while GIS can model the potential spread and impact of a flood.
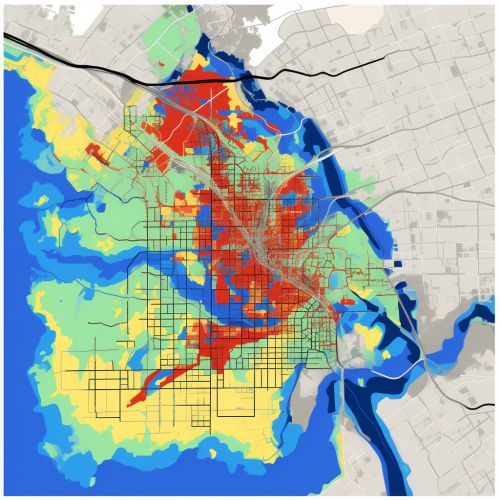
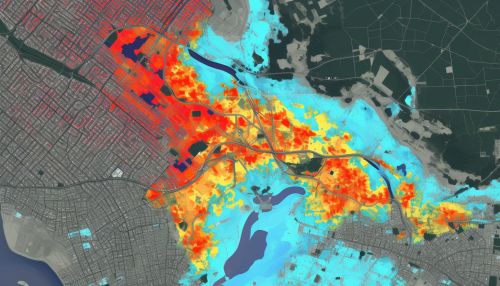
Vulnerability Assessment
Geoinformatics is also used in vulnerability assessment, which involves determining the susceptibility of a community or system to hazards. GIS can integrate various data, such as population density, infrastructure, and land use, to identify areas and populations at high risk. This information is crucial in prioritizing interventions and resources for disaster risk reduction.

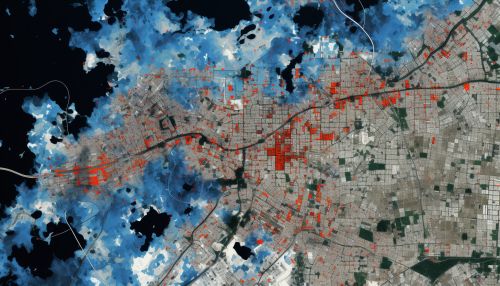
Mitigation Planning and Implementation
In the field of disaster risk reduction, mitigation refers to the efforts to reduce the risk of disasters by reducing vulnerability and enhancing capacity. Geoinformatics aids in the planning and implementation of mitigation strategies by providing spatial data and analysis. For instance, GIS can help in the design of evacuation routes, the selection of sites for emergency shelters, and the planning of land use to minimize exposure to hazards.
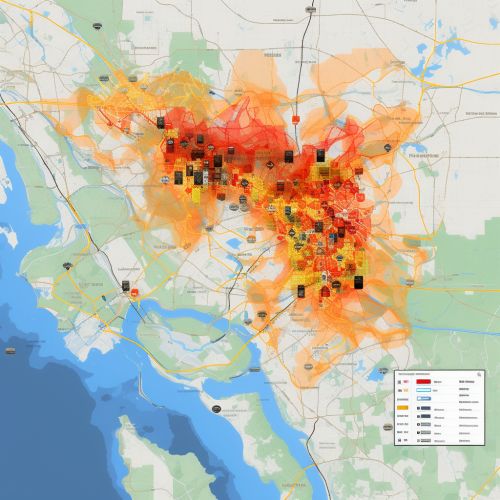

Benefits of Geoinformatics in Disaster Risk Reduction
The use of geoinformatics in disaster risk reduction offers several benefits. First, it provides accurate and up-to-date spatial data, which is essential in hazard and vulnerability assessment. Second, it allows for the integration and analysis of diverse data, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of disaster risks. Third, it enables the visualization of risks and mitigation strategies, aiding in communication and decision-making. Lastly, it supports the monitoring and evaluation of disaster risk reduction efforts, contributing to their improvement and effectiveness.
Challenges in the Use of Geoinformatics in Disaster Risk Reduction
Despite its benefits, the use of geoinformatics in disaster risk reduction also faces several challenges. These include the availability and quality of spatial data, the capacity to use geoinformatics tools and interpret their outputs, and the integration of geoinformatics into disaster risk reduction policies and practices. Addressing these challenges requires efforts in data collection and management, capacity building, and policy development.
Conclusion
Geoinformatics plays a pivotal role in disaster risk reduction, aiding in hazard and vulnerability assessment, mitigation planning and implementation, and monitoring and evaluation. While challenges exist, the benefits of geoinformatics in disaster risk reduction underscore its importance and potential. As technology advances and data becomes more accessible, the role of geoinformatics in disaster risk reduction is expected to grow, contributing to the resilience of communities and systems to disasters.


