The Role of Geoinformatics in Climate Change Mitigation
Introduction
Geoinformatics, often also referred to as geospatial informatics, is an interdisciplinary field that utilizes a broad range of tools and techniques from the geospatial sciences, including GIS, remote sensing, and GPS, to gather, analyze, and interpret geographic data. This data is then used to understand patterns, relationships, and trends on the Earth's surface. One of the most pressing applications of geoinformatics today is in the realm of climate change mitigation.


Geoinformatics and Climate Change
Climate change is a complex global issue that requires a comprehensive understanding of the Earth's systems and the impacts of human activities. Geoinformatics provides a powerful toolset for studying these systems and impacts, and for developing strategies to mitigate climate change.


Understanding Climate Change
Geoinformatics plays a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of climate change. It enables scientists to collect and analyze vast amounts of data about the Earth's climate system, including temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and sea level rise. This data can be used to create climate models that predict future climate scenarios based on different greenhouse gas emission pathways.


Monitoring Climate Change
Geoinformatics is also essential for monitoring changes in the Earth's climate. Remote sensing technologies, such as satellites, can provide continuous, real-time data on a global scale. This data can be used to monitor changes in sea ice extent, glacier retreat, deforestation, and other indicators of climate change.


Mitigating Climate Change
In addition to understanding and monitoring climate change, geoinformatics can also contribute to climate change mitigation efforts. GIS can be used to identify optimal locations for renewable energy installations, such as wind farms or solar panels. It can also be used to plan for reforestation efforts, carbon sequestration projects, and other mitigation strategies.


Geoinformatics Techniques in Climate Change Mitigation
Several geoinformatics techniques are particularly useful in climate change mitigation.
Geographic Information Systems
GIS is a powerful tool for managing and analyzing spatial data. It can be used to map the distribution of greenhouse gas emissions, identify areas of high vulnerability to climate change, and plan for climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
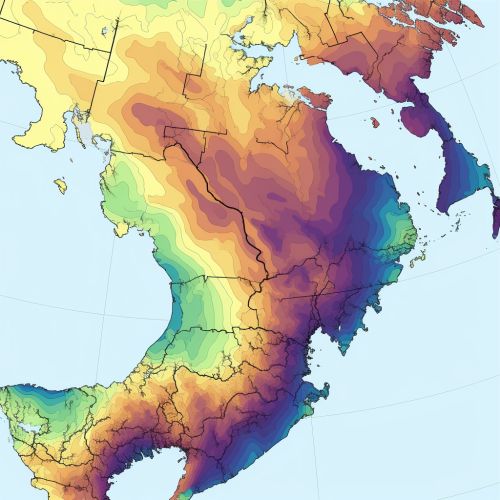
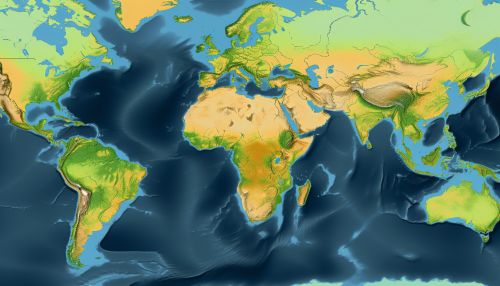
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing technologies, such as satellites and drones, can provide detailed, up-to-date information on the Earth's surface. This information can be used to monitor changes in land use, vegetation cover, and other factors that contribute to climate change.


Climate Modeling
Climate models are mathematical representations of the Earth's climate system. They can be used to predict future climate scenarios based on different greenhouse gas emission pathways. These predictions can inform policy decisions and mitigation strategies.


Challenges and Future Directions
While geoinformatics offers powerful tools for climate change mitigation, it also presents several challenges. These include the need for high-quality, up-to-date data; the complexity of integrating different types of data; and the need for advanced computational resources and expertise.
Despite these challenges, the field of geoinformatics is rapidly evolving, and new technologies and techniques are continually being developed. These advancements promise to further enhance our ability to understand, monitor, and mitigate climate change.


