History of radiology
Early Beginnings
The history of radiology can be traced back to the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895. Roentgen, a German physicist, was experimenting with cathode rays when he discovered a new type of ray that could penetrate solid objects and leave an image on photographic plates. This discovery, which he named "X-rays", marked the birth of radiology as a medical specialty.
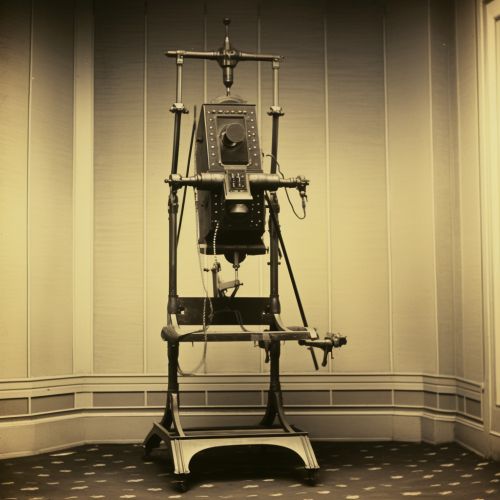
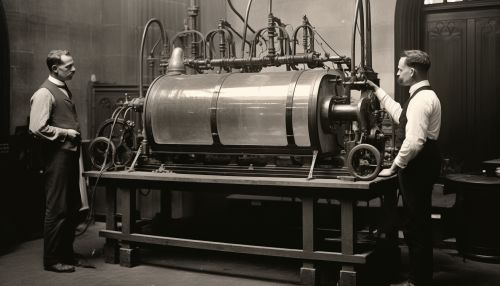
Development of Radiology
Following Roentgen's discovery, the potential of X-rays for medical diagnosis and treatment was quickly recognized. In the early 20th century, radiology was primarily used for diagnostic purposes, with the development of fluoroscopic techniques and contrast media allowing for more detailed imaging of the body's internal structures.
The 1920s and 1930s saw significant advancements in radiology technology, including the development of mobile X-ray units and the introduction of radiographic film. These advancements allowed for greater flexibility in imaging and improved the quality of radiographic images.
Mid-20th Century Advancements
The mid-20th century brought about significant advancements in radiology, particularly in the field of therapeutic radiology. The development of high-energy linear accelerators in the 1950s allowed for the precise delivery of radiation to tumors, marking the beginning of modern radiation therapy.
During this time, the field of diagnostic radiology also saw significant advancements. The development of computed tomography (CT) in the 1970s revolutionized the field by providing detailed, cross-sectional images of the body. This was followed by the introduction of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in the 1980s, which provided even more detailed images without the use of ionizing radiation.
Modern Radiology
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, radiology has continued to evolve and expand. The introduction of digital imaging and the development of advanced imaging techniques, such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and ultrasound, have further broadened the scope of radiology.
Today, radiology plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. From detecting cancers and diagnosing heart disease to guiding minimally invasive surgical procedures, the applications of radiology are vast and continually expanding.
Future of Radiology
The future of radiology is likely to be shaped by advancements in technology and the increasing integration of artificial intelligence in imaging analysis. As imaging techniques continue to evolve, radiology will continue to play a vital role in healthcare, providing valuable insights into the human body and aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of disease.
