The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Forest Fires
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics that deals with spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. It has been widely used in various fields such as mining, hydrogeology, and environmental science. In recent years, its application in predicting forest fires has gained significant attention. This article explores the role of geostatistics in predicting forest fires, providing an in-depth understanding of the methodologies involved and the importance of this field in forest fire management.


Geostatistics: An Overview
Geostatistics originated from the mining and petroleum industry, where it was used to estimate the likely location of valuable resources. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of quantitative data related to spatial or spatiotemporal phenomena. The primary goal of geostatistics is to predict the values of a random field at unobserved locations based on observed data.


Geostatistical Techniques in Predicting Forest Fires
Several geostatistical techniques have been employed in predicting forest fires. These include:
Kriging
Kriging is a geostatistical interpolation technique that predicts the value of a variable at an unobserved location based on the values at observed locations. In the context of forest fires, kriging can be used to predict the likelihood of a fire occurring in a specific area based on past fire occurrences and environmental factors.
Point Process Models
Point process models are used to analyze the spatial distribution of events. In forest fire prediction, point process models can be used to analyze the spatial distribution of past fire occurrences and predict the likelihood of future fires.
Geographically Weighted Regression
Geographically weighted regression (GWR) is a local version of spatial regression that allows the relationships between variables to vary across space. GWR can be used to identify the local factors that influence the likelihood of forest fires.
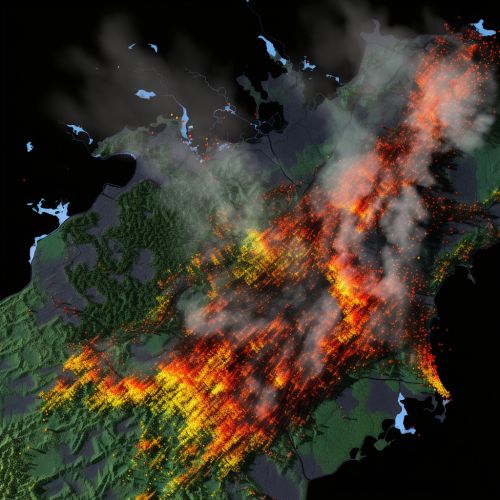

Importance of Geostatistics in Forest Fire Prediction
The application of geostatistics in forest fire prediction has several benefits:
Improved Accuracy
Geostatistical techniques can improve the accuracy of forest fire predictions by taking into account the spatial and temporal patterns of past fire occurrences and environmental factors.
Risk Assessment
Geostatistics can be used to assess the risk of forest fires in different areas, which can inform fire management strategies and resource allocation.
Prevention and Control
By predicting the likelihood of forest fires, geostatistics can aid in the development of prevention and control strategies, such as controlled burns and firebreaks.

Future Directions
As geostatistical techniques continue to evolve, their application in forest fire prediction is likely to become more sophisticated. Future research may focus on integrating geostatistics with other predictive models, such as machine learning algorithms, to improve the accuracy and precision of forest fire predictions.
