The Role of Geoinformatics in Urban Ecology
Introduction
Geoinformatics, also known as geospatial informatics, is an interdisciplinary field that uses a wide range of technologies to gather, store, process, and deliver geographic information. In the context of Urban Ecology, geoinformatics plays a pivotal role in understanding and managing urban environments. This article delves into the intricate relationship between geoinformatics and urban ecology, exploring how the former aids in the study and preservation of the latter.


Geoinformatics: An Overview
Geoinformatics is a branch of science that deals with the study and application of geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, global positioning systems (GPS), and other related technologies. The primary goal of geoinformatics is to develop and use these technologies to collect, analyze, and interpret spatial data. This field has found applications in various domains, including environmental management, urban planning, transportation, and more.
Urban Ecology: An Overview
Urban ecology is a subfield of ecology that studies the relationship between humans and their urban environments. It involves the study of the distribution, abundance, and interactions of organisms in urban settings. Urban ecology aims to understand how human activities impact urban ecosystems and how these ecosystems, in turn, influence the health and well-being of urban populations.


The Intersection of Geoinformatics and Urban Ecology
The integration of geoinformatics and urban ecology provides a powerful tool for understanding and managing urban ecosystems. Geoinformatics technologies such as GIS and remote sensing allow scientists to collect and analyze spatial data on a large scale, providing valuable insights into the structure and function of urban ecosystems.
GIS in Urban Ecology
GIS is a powerful tool that allows researchers to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial data. In urban ecology, GIS is used to map and monitor urban green spaces, assess the impact of urban development on biodiversity, and plan for sustainable urban growth. For instance, GIS can be used to identify areas of high biodiversity within a city, allowing urban planners to prioritize these areas for conservation.

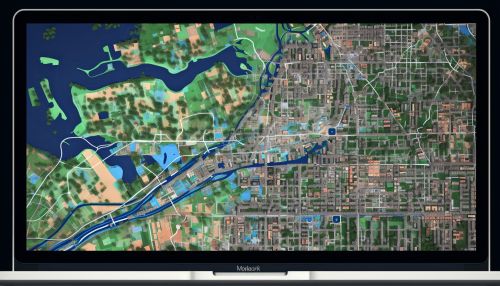
Remote Sensing in Urban Ecology
Remote sensing is another crucial technology in the field of urban ecology. It involves the use of satellites or aircraft to collect data about the Earth's surface. This technology allows researchers to monitor urban growth, assess the health of urban green spaces, and detect changes in land use. For example, remote sensing can be used to monitor the spread of urban heat islands, which are areas of a city that are significantly warmer than their surroundings due to human activities.


Applications of Geoinformatics in Urban Ecology
Geoinformatics technologies have a wide range of applications in urban ecology. These include urban planning, biodiversity conservation, climate change adaptation, and more.
Urban Planning
In the field of urban planning, geoinformatics technologies such as GIS and remote sensing are used to map and monitor urban growth, assess the impact of urban development on the environment, and plan for sustainable urban growth. For instance, GIS can be used to identify areas of a city that are suitable for development, while remote sensing can be used to monitor the impact of development on the urban environment.


Biodiversity Conservation
Geoinformatics also plays a crucial role in biodiversity conservation in urban areas. GIS and remote sensing technologies can be used to identify and monitor areas of high biodiversity within a city, allowing conservationists to prioritize these areas for protection. Additionally, these technologies can be used to assess the impact of urban development on biodiversity and to develop strategies for mitigating this impact.


Climate Change Adaptation
With the increasing threat of climate change, geoinformatics technologies are being used to help cities adapt to changing climate conditions. For example, GIS can be used to map areas of a city that are vulnerable to flooding, allowing city planners to develop strategies for reducing flood risk. Similarly, remote sensing can be used to monitor the impact of climate change on urban green spaces, providing valuable data for climate change adaptation planning.


Challenges and Future Directions
While geoinformatics has significantly contributed to the field of urban ecology, there are still challenges to be addressed. These include the need for more accurate and high-resolution spatial data, the integration of different types of data, and the development of more sophisticated analytical tools. Despite these challenges, the future of geoinformatics in urban ecology looks promising, with advances in technology and data analysis methods expected to provide even more detailed and accurate insights into urban ecosystems.
