The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Water Availability
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics that deals with spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including petroleum geology, hydrology, meteorology, and environmental science. In the context of water availability, geostatistics plays a crucial role in predicting the spatial distribution of water resources, which is essential for planning and managing water supply.


Geostatistical Analysis
Geostatistical analysis involves the use of statistical methods for the interpretation of spatial data. These methods are used to predict the values of a variable at unobserved locations based on observations at other locations. In the context of water availability, geostatistical analysis is used to predict the distribution of water resources, such as groundwater, surface water, and soil moisture, across a geographical area.


Spatial Continuity
One of the key concepts in geostatistics is spatial continuity, which refers to the degree of correlation between values at different locations. This concept is often quantified using a variogram, which is a plot of the variance of differences between values at pairs of locations as a function of the distance and direction separating the pairs. In the context of water availability, spatial continuity can help in understanding the spatial distribution of water resources.


Interpolation Techniques
Geostatistics employs various interpolation techniques to predict values at unobserved locations based on observed data. These techniques include kriging, inverse distance weighting (IDW), and radial basis functions (RBF). Kriging, in particular, is a popular geostatistical interpolation technique that provides best linear unbiased predictions (BLUPs) based on the variogram and the spatial arrangement of the data.
Application in Predicting Water Availability
Geostatistics is extensively used in predicting water availability. It provides a robust framework for analyzing spatial data related to water resources and predicting their distribution across a geographical area. This is particularly important for water resource management, as it helps in planning and managing water supply, especially in regions where water resources are scarce or unevenly distributed.


Groundwater Modeling
One of the key applications of geostatistics in predicting water availability is groundwater modeling. Geostatistical methods are used to analyze spatial data related to groundwater, such as the distribution of aquifers, groundwater levels, and groundwater quality. This information is used to predict the availability of groundwater resources and to plan for their sustainable use.
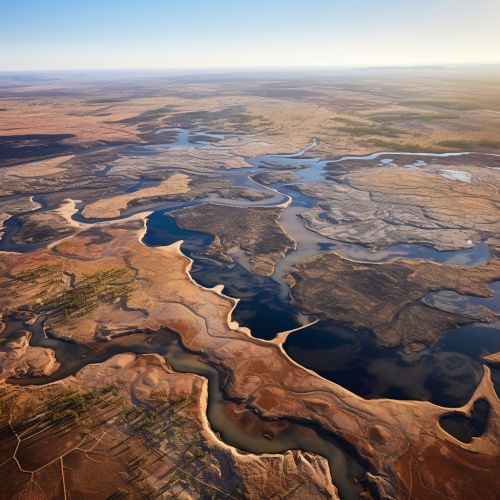


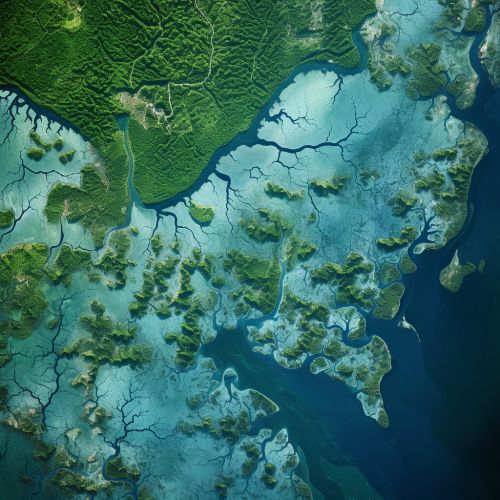
Surface Water Assessment
Geostatistics is also used in the assessment of surface water resources. It is used to analyze spatial data related to surface water, such as the distribution of rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, and the flow rates and water quality of these water bodies. This information is used to predict the availability of surface water resources and to plan for their management.


Soil Moisture Estimation
Another application of geostatistics in predicting water availability is soil moisture estimation. Geostatistical methods are used to analyze spatial data related to soil moisture, which is a key factor in determining the availability of water for agricultural use. This information is used to predict the spatial distribution of soil moisture and to plan for irrigation and other agricultural practices.


Conclusion
Geostatistics plays a crucial role in predicting water availability. By providing a robust framework for analyzing spatial data related to water resources, it helps in predicting their distribution across a geographical area. This is particularly important for water resource management, as it helps in planning and managing water supply, especially in regions where water resources are scarce or unevenly distributed.
