The Role of Geoinformatics in Predicting Hurricane Risk
Introduction
Geoinformatics, also known as geospatial informatics, is an interdisciplinary field that uses a range of technologies to gather, analyze, manage, and present geographic data. In the context of predicting hurricane risk, geoinformatics plays a crucial role in providing accurate, timely, and comprehensive information that can help mitigate the impact of these natural disasters.
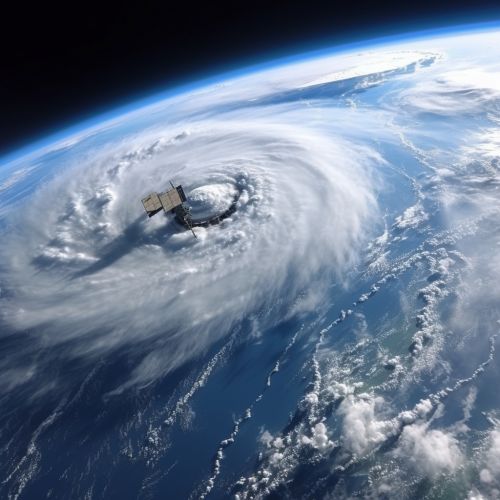


Geoinformatics and Hurricane Prediction
Hurricane prediction involves the use of various tools and methodologies to forecast the trajectory, intensity, and potential impact of a hurricane. Geoinformatics, through the use of technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Remote Sensing, and Global Positioning Systems (GPS), provides a platform for the collection, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data related to hurricanes.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS is a tool that allows for the management, analysis, and display of geographic data. In hurricane prediction, GIS can be used to analyze historical hurricane data, track the path of active hurricanes, and model potential hurricane paths based on current atmospheric conditions. GIS can also be used to identify areas at high risk of hurricane impact based on factors such as proximity to the coast, elevation, and population density.
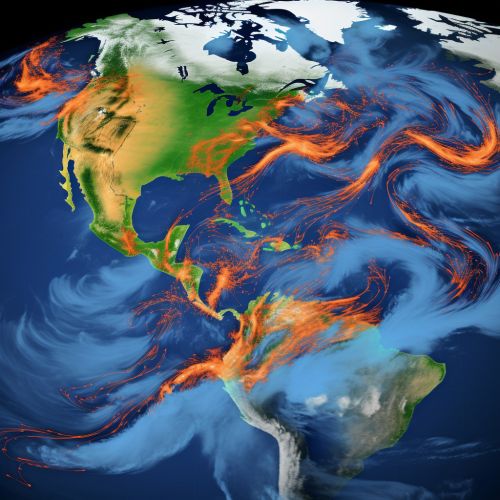
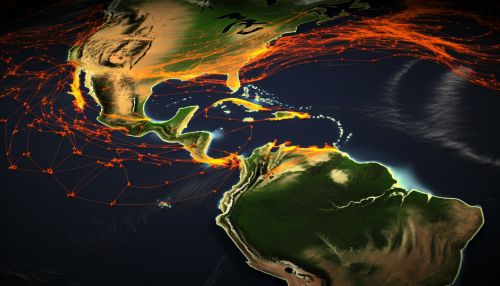
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing involves the use of satellites or aircraft to collect data about the earth's surface. In the context of hurricane prediction, remote sensing technologies such as weather satellites and radar are used to monitor atmospheric conditions, track the development and movement of hurricanes, and measure variables such as wind speed, precipitation, and sea surface temperature that are critical in predicting hurricane behavior.
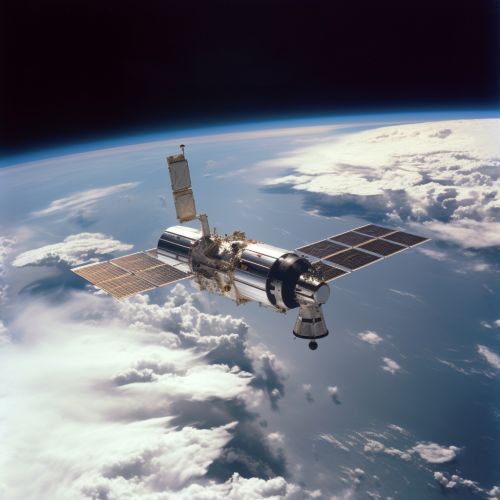


Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
GPS technology, while primarily known for its navigation capabilities, also plays a significant role in hurricane prediction. GPS can provide precise measurements of atmospheric pressure, temperature, and humidity, which are essential parameters in hurricane forecasting models. Additionally, GPS can be used to track the movement of hurricanes in real time, providing valuable data for predicting the path and intensity of these storms.


The Role of Geoinformatics in Hurricane Risk Assessment
Beyond predicting the path and intensity of hurricanes, geoinformatics also plays a key role in assessing the potential risk and impact of these storms. This involves analyzing a range of factors, including the physical characteristics of the hurricane, the vulnerability of the population and infrastructure, and the capacity of the community to respond and recover.
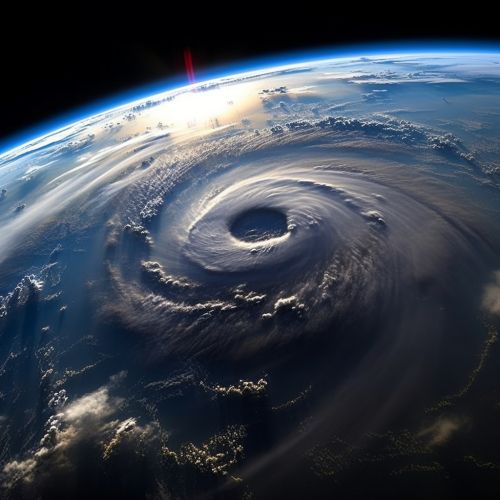
Physical Characteristics of the Hurricane
Geoinformatics tools such as GIS and remote sensing can provide detailed information on the physical characteristics of a hurricane, including its size, intensity, speed, and trajectory. This information is crucial in assessing the potential impact of the hurricane, as it can help determine the areas that are likely to be affected and the severity of the impact.


Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment involves analyzing the susceptibility of a community or region to the impact of a hurricane. This can include factors such as population density, the age and health of the population, the quality and type of housing, and the presence of critical infrastructure such as hospitals and power plants. Geoinformatics can provide the tools to collect, analyze, and visualize this data, helping to identify areas of high vulnerability and prioritize mitigation efforts.
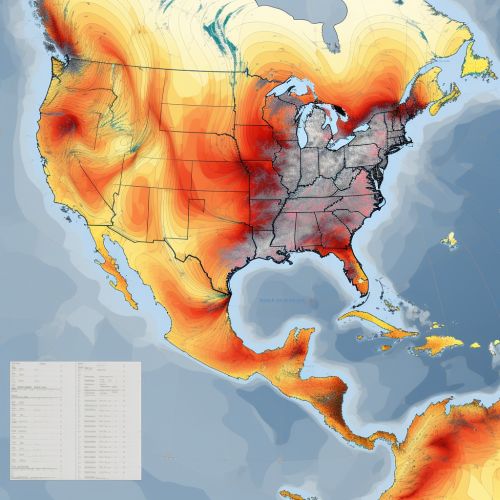
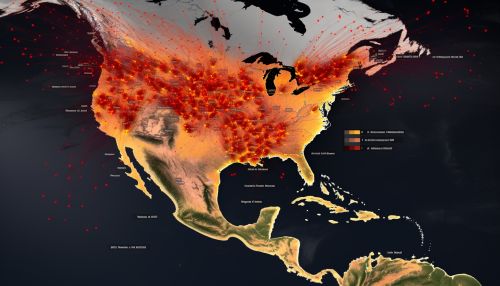
Capacity Assessment
Capacity assessment involves evaluating the ability of a community or region to respond to and recover from a hurricane. This can include factors such as the availability of emergency services, the robustness of the infrastructure, and the level of disaster preparedness among the population. Again, geoinformatics can provide valuable tools for collecting and analyzing this data, helping to identify areas of low capacity and target resources where they are most needed.


Conclusion
In conclusion, geoinformatics plays a crucial role in predicting hurricane risk. Through the use of technologies such as GIS, remote sensing, and GPS, geoinformatics provides the tools to collect, analyze, and visualize a wide range of data related to hurricanes. This information can be used to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes, assess the vulnerability and capacity of communities, and ultimately help mitigate the impact of these devastating natural disasters.
