The Role of Geoinformatics in Forest Management
Introduction
Geoinformatics, a discipline that combines geospatial analysis and informatics, plays a crucial role in forest management. It involves the use and application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and GPS to collect, analyze, and interpret data related to the earth's surface. This data is then used to make informed decisions about the management and conservation of forests.


Geoinformatics and Forest Management
Forest management involves the application of various scientific, economic, and social principles to the process of managing forests. It is a broad term that encompasses a range of activities, including timber harvesting, wildlife habitat management, and forest conservation. Geoinformatics provides a powerful toolset for forest managers, enabling them to collect and analyze spatial data, model forest dynamics, and make informed decisions about forest management strategies.
Data Collection
One of the primary uses of geoinformatics in forest management is data collection. Remote sensing technologies, such as satellites and drones, are used to collect data on a variety of forest attributes, including tree species, tree density, and forest health. This data is then analyzed using GIS software, which allows forest managers to visualize and interpret the data in a spatial context.
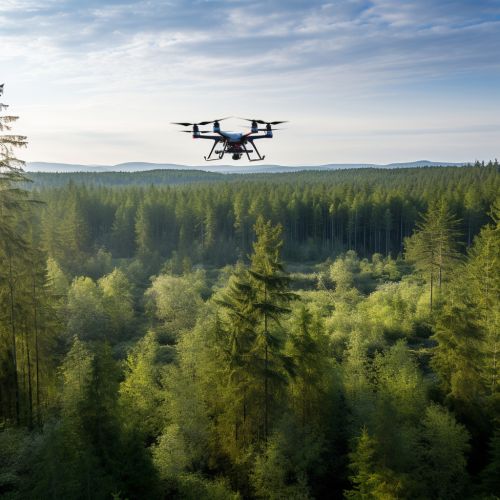


Forest Modeling
Another important application of geoinformatics in forest management is forest modeling. GIS software can be used to create spatial models of forests, which can help forest managers predict how forests will respond to different management strategies or environmental changes. For example, a forest manager might use a GIS model to predict how a forest will respond to a proposed timber harvesting plan, or how it might be affected by climate change.
Decision Making
Geoinformatics also plays a crucial role in decision making in forest management. By providing a visual representation of forest data, GIS can help forest managers make informed decisions about a range of issues, from where to harvest timber to how to manage wildlife habitat. In addition, GIS can be used to create maps and other visual aids that can be used in presentations and reports, helping to communicate complex forest management issues to stakeholders and the public.

Challenges and Opportunities
While geoinformatics offers many benefits for forest management, it also presents some challenges. One of the main challenges is the need for high-quality, up-to-date spatial data. Collecting this data can be time-consuming and expensive, and in some cases, the necessary data may not be available at all. However, advances in remote sensing technology are making it easier and more affordable to collect high-quality spatial data.
Another challenge is the need for specialized skills and training to use GIS and remote sensing technologies effectively. However, many universities and colleges now offer courses and programs in geoinformatics, helping to train the next generation of forest managers in these important tools.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by geoinformatics for forest management are immense. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the use of geoinformatics in forest management will only continue to grow.


Conclusion
Geoinformatics plays a vital role in modern forest management, providing the tools necessary to collect, analyze, and interpret spatial data. By enabling forest managers to visualize and model forest dynamics, geoinformatics helps to inform decision making and improve the effectiveness of forest management strategies. Despite the challenges associated with data collection and the need for specialized skills, the benefits of geoinformatics for forest management are clear.
