The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Oceanic Productivity
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics that deals with spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. It has been widely used in a variety of disciplines, including geology, petroleum engineering, hydrogeology, and environmental science. In recent years, the application of geostatistics in predicting oceanic productivity has gained significant attention. This article provides a comprehensive and detailed exploration of the role of geostatistics in predicting oceanic productivity, delving deeper than general summaries to provide expert-level information.


Geostatistics: An Overview
Geostatistics originated from the mining and petroleum industry, where it was used to predict the likelihood of finding valuable resources such as oil or minerals. It is a discipline that focuses on the statistical analysis of spatial and spatiotemporal data. The primary objective of geostatistics is to predict the values of a random field at unobserved locations based on observations at known locations. This is achieved through the use of mathematical models that take into account the spatial correlation between data points.


Oceanic Productivity
Oceanic productivity refers to the amount of life that an ocean area can support. It is a critical aspect of the global carbon cycle and plays a significant role in climate regulation. The primary producers in the ocean, mainly phytoplankton, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, thereby reducing greenhouse gas levels. The productivity of the ocean is influenced by various factors, including light availability, nutrient concentration, and water temperature.

The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Oceanic Productivity
Geostatistics has been increasingly used to predict oceanic productivity due to its ability to handle spatially correlated data. The spatial distribution of oceanic productivity is not random but exhibits a certain degree of spatial correlation. For instance, areas with similar environmental conditions tend to have similar productivity levels. Geostatistics provides a mathematical framework to quantify this spatial correlation and use it to predict productivity at unobserved locations.
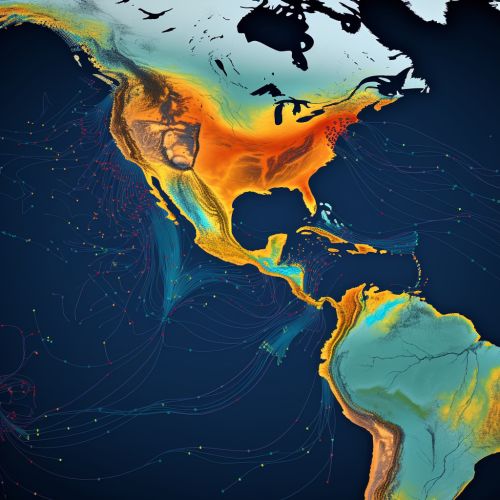
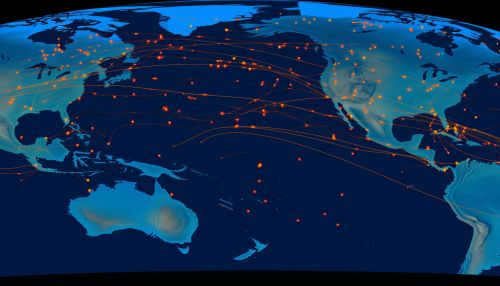
Application of Geostatistics in Oceanic Productivity Prediction
The application of geostatistics in predicting oceanic productivity involves several steps. First, data on oceanic productivity and influencing factors are collected from various sources, such as satellite imagery and oceanographic surveys. These data are then analyzed to identify spatial patterns and correlations. Next, a geostatistical model is developed to predict productivity at unobserved locations based on the observed data. Finally, the model's predictions are validated using independent data sets.


Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising applications of geostatistics in predicting oceanic productivity, several challenges remain. These include the lack of high-quality spatial data, the complexity of oceanic ecosystems, and the uncertainty associated with geostatistical models. Future research should focus on addressing these challenges and improving the accuracy and reliability of geostatistical predictions.


