The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Flood Risk
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics that deals with spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. It has been widely used in various fields such as mining, hydrogeology, and environmental science. In the context of flood risk prediction, geostatistics plays a crucial role in understanding the spatial variability of hydrological parameters, which is essential for accurate flood prediction and management.
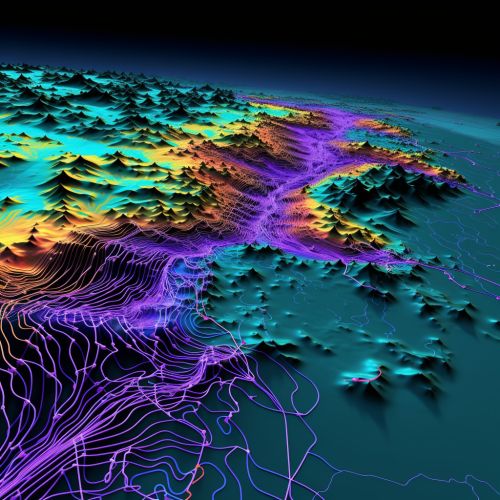

Geostatistics: An Overview
Geostatistics originated from the mining and petroleum industries, where it was used to estimate the likely location of valuable resources. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of spatially referenced data. The primary goal of geostatistics is to predict the values of a random variable at unobserved locations, based on observations at known locations. This is achieved through the use of statistical models that incorporate spatial correlation structures.
Role of Geostatistics in Flood Risk Prediction
Geostatistics plays a significant role in predicting flood risk due to its ability to handle spatially correlated data. This is particularly important in hydrology, where spatial correlation is often strong. For example, rainfall intensity and river flow rates at nearby locations are typically highly correlated. By taking into account this spatial correlation, geostatistics allows for more accurate prediction of flood risk.


Spatial Variability of Hydrological Parameters
In flood risk prediction, it is crucial to understand the spatial variability of hydrological parameters such as rainfall intensity, river flow rates, and soil moisture content. These parameters can vary greatly over space, and their spatial distribution is often highly complex. Geostatistics provides tools for characterizing this spatial variability, such as variograms and kriging.


Flood Prediction Models
Geostatistics is often used in conjunction with hydrological models to predict flood risk. These models simulate the movement of water through a catchment, taking into account factors such as rainfall, evaporation, and infiltration. Geostatistical techniques can be used to estimate the parameters of these models, as well as to quantify the uncertainty in the predictions.


Flood Risk Mapping
One of the key applications of geostatistics in flood risk prediction is the creation of flood risk maps. These maps show the probability of flooding in different areas, based on a combination of hydrological parameters and topographical data. Geostatistical techniques can be used to interpolate these parameters across the study area, resulting in a detailed and accurate flood risk map.
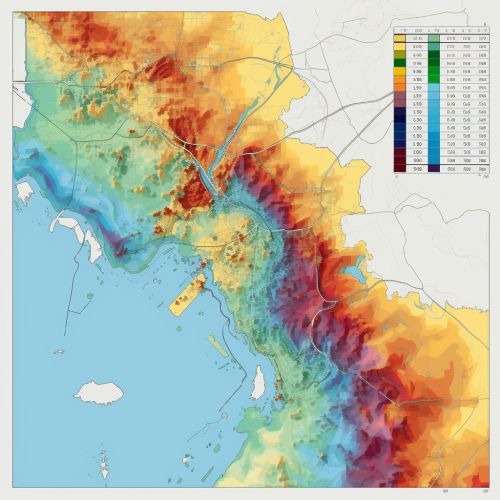
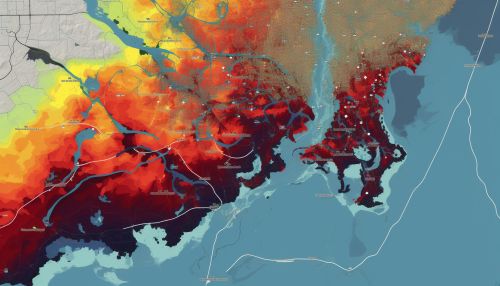
Conclusion
Geostatistics plays a vital role in predicting flood risk, providing tools for understanding the spatial variability of hydrological parameters and for creating accurate flood risk maps. By incorporating spatial correlation structures, geostatistics allows for more accurate and reliable flood predictions, contributing to more effective flood management strategies.
