The Role of Geostatistics in Environmental Impact Assessment
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including petroleum geology, hydrogeology, hydrology, meteorology, oceanography, geochemistry, geometallurgy, geography, forestry, environmental control, landscape ecology, soil science, and agriculture (crop yield estimation). Geostatistics is applied in varied branches of geography, particularly those involving the spread of diseases (epidemiology), the practice of commerce and military (logistics), and the development of efficient spatial networks.

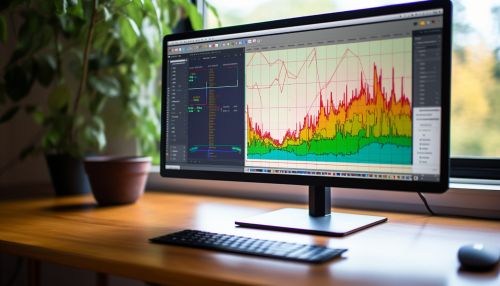
Environmental Impact Assessment and Geostatistics
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a process of evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed project or development, taking into account inter-related socio-economic, cultural and human-health impacts, both beneficial and adverse. Geostatistics plays a crucial role in EIA by providing the tools and techniques to analyze and interpret environmental data, and to predict future scenarios based on this data.
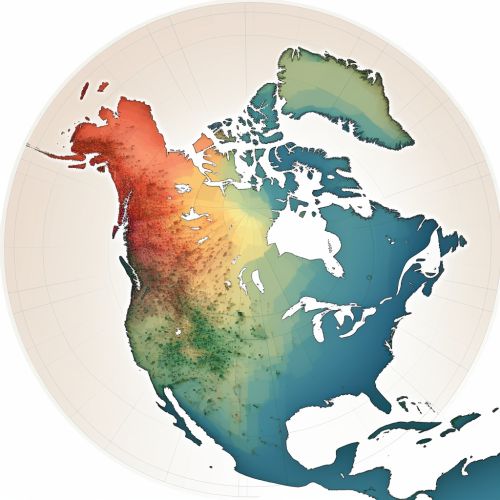
Geostatistical Tools and Techniques
Geostatistics offers a range of tools and techniques for analyzing spatial data. These include variogram modeling, kriging, spatial point pattern analysis, and geographically weighted regression. These techniques allow for the prediction of spatial patterns and the estimation of uncertainty, which are critical in environmental impact assessment.

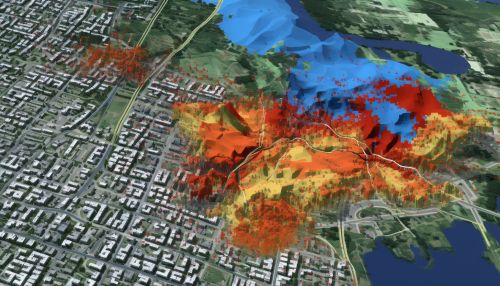
Applications of Geostatistics in EIA
Geostatistics is used in EIA in several ways. It can be used to identify and quantify spatial patterns in environmental data, to predict the likely impacts of a proposed development on these patterns, and to monitor changes in these patterns over time. This can help to inform decision-making and to ensure that the potential impacts of a development are properly managed.

Challenges and Limitations
While geostatistics provides a powerful tool for environmental impact assessment, it also presents a number of challenges and limitations. These include the need for large amounts of high-quality data, the complexity of the techniques, and the difficulty of interpreting the results. Despite these challenges, the use of geostatistics in EIA is likely to continue to grow as the demand for accurate and reliable environmental data increases.


Future Directions
The future of geostatistics in environmental impact assessment is likely to be shaped by advances in technology, particularly in the areas of data collection and analysis. This includes the development of more sophisticated geostatistical models, the use of machine learning techniques, and the integration of geostatistics with other forms of spatial analysis.


