The Role of Geoinformatics in Predicting Flood Risk
Introduction
Geoinformatics, a discipline that uses Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and other geospatial technologies, plays a crucial role in predicting flood risk. This field of study involves the gathering, storing, processing, and delivering of geographic information. It is a powerful tool for flood risk management as it allows for the analysis of spatial data, which is essential in understanding flood patterns and predicting future flood events.


Geoinformatics and Flood Risk Prediction
The application of geoinformatics in predicting flood risk involves the use of various geospatial technologies, including GIS, remote sensing, and Global Positioning System (GPS). These technologies enable the collection and analysis of data related to the physical characteristics of a region, such as topography, land use, and soil type, which are critical factors in flood risk assessment.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
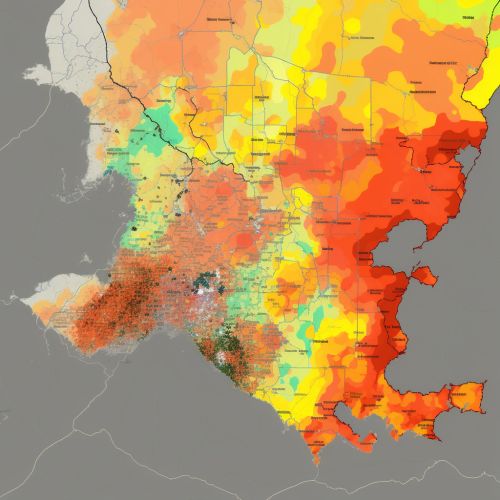
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a powerful tool used in geoinformatics that allows for the visualization, analysis, and interpretation of data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends. In the context of flood risk prediction, GIS can be used to create flood maps, which are essential in identifying areas prone to flooding. These maps can be used by decision-makers and stakeholders for planning and implementing flood risk management strategies.


Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is another geospatial technology used in geoinformatics for flood risk prediction. It involves the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object. In flood risk prediction, remote sensing can be used to monitor rainfall patterns, river flow, and changes in land use, which are all critical factors in flood risk assessment.


Global Positioning System (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth. In flood risk prediction, GPS can be used to accurately measure the elevation of land, which is a critical factor in determining flood risk.


Flood Risk Assessment Using Geoinformatics
Flood risk assessment is a complex process that involves the identification of flood-prone areas, the evaluation of the potential consequences of flooding, and the estimation of the probability of flood occurrence. Geoinformatics provides the tools and techniques necessary for conducting a comprehensive flood risk assessment.
Identification of Flood-Prone Areas
The first step in flood risk assessment is the identification of flood-prone areas. This involves the analysis of spatial data related to the physical characteristics of a region, such as topography, land use, and soil type. GIS and remote sensing technologies are used to collect and analyze this data, and to create flood maps that identify areas prone to flooding.
Evaluation of Potential Consequences of Flooding
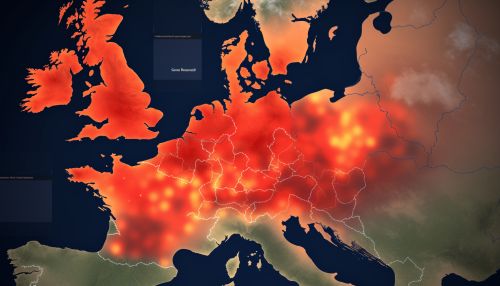
The next step in flood risk assessment is the evaluation of the potential consequences of flooding. This involves the analysis of data related to the vulnerability of the population and infrastructure in the identified flood-prone areas. GIS can be used to analyze this data and to create vulnerability maps that identify areas at high risk of damage in the event of a flood.
Estimation of Probability of Flood Occurrence
The final step in flood risk assessment is the estimation of the probability of flood occurrence. This involves the analysis of historical flood data and climate data to predict future flood events. GIS and remote sensing technologies are used to analyze this data and to create flood risk maps that estimate the probability of flood occurrence in the identified flood-prone areas.
Conclusion
The role of geoinformatics in predicting flood risk is critical in today's world where climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of flood events. Through the use of geospatial technologies such as GIS, remote sensing, and GPS, geoinformatics provides the tools and techniques necessary for conducting a comprehensive flood risk assessment. This allows for the identification of flood-prone areas, the evaluation of the potential consequences of flooding, and the estimation of the probability of flood occurrence, which are all essential for planning and implementing effective flood risk management strategies.
