Transesophageal Echocardiogram
Overview
A Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is a specialized procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves, or ultrasound, to produce detailed images of the heart and its blood vessels. This non-invasive procedure provides a closer and more accurate view of the heart than a standard echocardiogram, as the esophagus is located directly behind the heart.
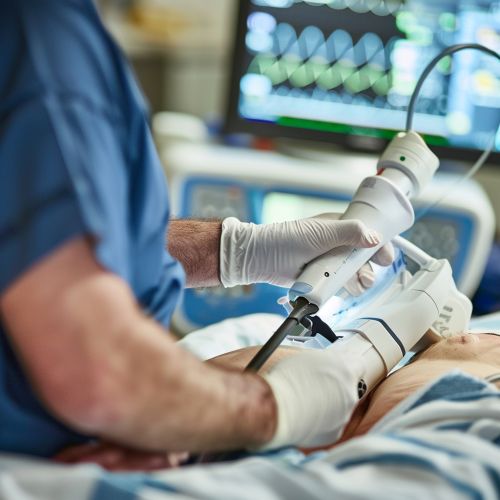
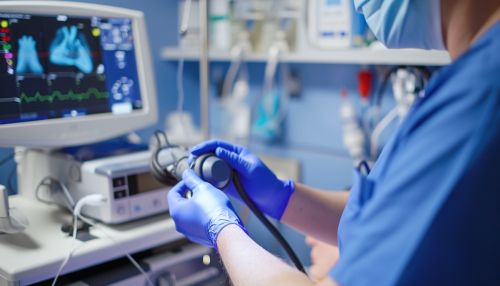
Procedure
The TEE procedure begins with the administration of a local anesthetic to numb the throat and a mild sedative to help the patient relax. A small, flexible tube containing an ultrasound transducer is then passed through the mouth, down the esophagus, and positioned near the heart. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the heart and are picked up by the transducer to create a moving image of the heart and its blood vessels on a monitor.
Indications
TEE is often used when a standard echocardiogram does not provide sufficient information or when a more detailed view of certain areas of the heart is required. It can be used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including valve disease, atrial fibrillation, and congenital heart defects. It can also be used to guide the surgeon during certain heart surgeries.
Risks and Complications
While TEE is generally safe, it does carry some risks. These include minor complications such as throat discomfort or minor bleeding, and more serious complications such as esophageal perforation or adverse reactions to the sedative. However, these serious complications are rare.
Interpretation of Results
The images obtained during a TEE provide detailed information about the size and shape of the heart, the functioning of the heart valves, and the movement of blood through the heart. This information can help to diagnose heart conditions, guide treatment decisions, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
