Tissues
Introduction
Tissues are collections of similar cells that perform a specific function in an organism. The study of tissue is known as histology, a branch of biology. Tissues can be classified into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
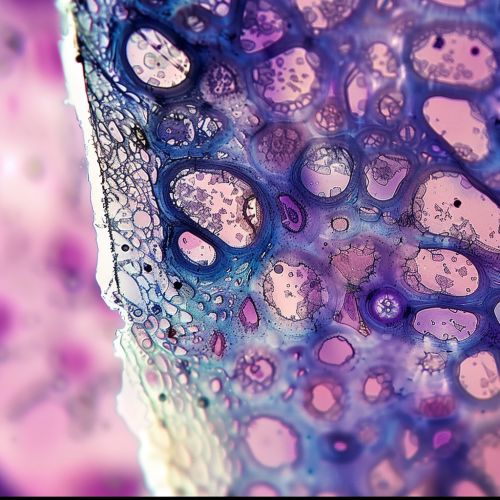

Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue, also known as epithelium, forms the outer layer of the skin and the inner lining of body cavities, blood vessels, and organs. It serves as a protective barrier against physical damage and microbial invasion. Epithelial tissue also plays a role in absorption, secretion, and sensation. It can be further classified based on the number of cell layers (simple or stratified) and cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, or columnar).
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue provides support and structure to the body. It includes various types such as bone, cartilage, adipose tissue, blood, and lymph. Connective tissue consists of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix, which can be either liquid (as in blood), jelly-like (as in cartilage), or solid (as in bone).
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement in the body. It can be classified into three types: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and causes voluntary movements. Cardiac muscle makes up the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, and blood vessels.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is specialized for communication. It consists of neurons, which transmit electrical signals, and neuroglia, which provide support and protection for neurons. Nervous tissue forms the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Tissue repair and regeneration is a complex process that involves cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. The ability of a tissue to repair or regenerate depends on its cell type. For example, epithelial and connective tissues have a high capacity for regeneration, while cardiac and nervous tissues have a limited capacity.
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a multidisciplinary field that aims to develop functional tissues for the replacement or repair of diseased or damaged tissues. It involves the use of cells, scaffolds, and biologically active molecules to create tissues in vitro that can be implanted into the body.
