Biology
Introduction
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical composition, function, development, and evolution. It is a natural science that encompasses all aspects of life, from the molecular level to the biosphere. The term "biology" is derived from the Greek words "bios" (life) and "logos" (study), and it was first used in the late 18th century.
Branches of Biology
Biology is a broad and diverse field, divided into several branches based on the type of organism and level of organization. Some of the main branches include:
- Microbiology: The study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi, and protozoa.
- Botany: The study of plants, including their physiology, classification, ecology, and distribution.
- Zoology: The study of animals, including their physiology, classification, habits, and distribution.
- Genetics: The study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in living organisms.
- Ecology: The study of the interactions between organisms and their environment.


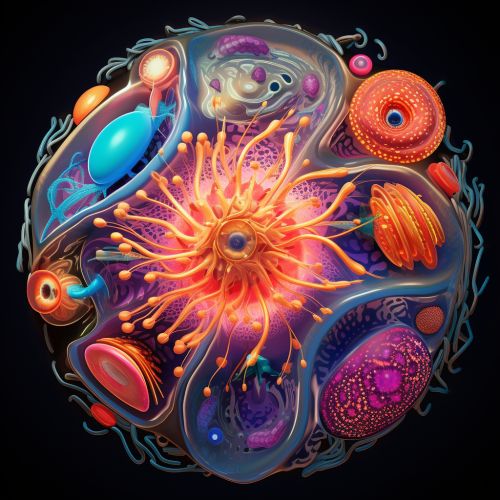
Cell Biology
At the heart of biology is the study of the basic unit of life, the cell. Cells are the smallest structures capable of basic life processes, such as metabolism and reproduction. The study of cells is known as cell biology or cytology.
Cells can be categorized into two types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archaea, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have a nucleus and other organelles.

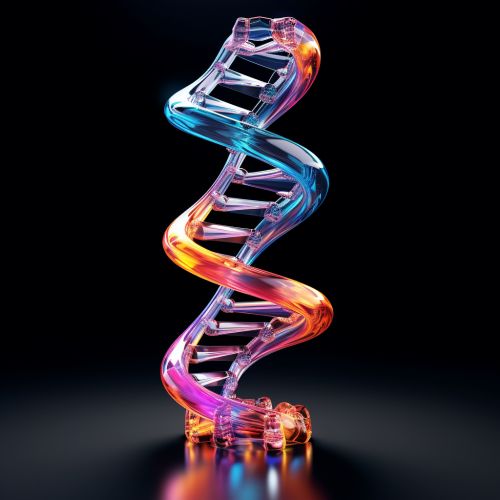
Genetics
Genetics is the branch of biology that studies genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. It seeks to understand the process of trait inheritance from parents to offspring, including the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior in the context of a cell or organism, gene distribution, and variation and change in populations.
The discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule, the genetic material of all organisms, was a significant milestone in genetics. This discovery led to the development of molecular biology, an interdisciplinary field that combines genetics and biochemistry.


Ecology
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies the interactions between organisms and their physical environment. It involves understanding biotic and abiotic factors influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms, the interactions among and between organisms in an ecosystem, and the dynamics of ecosystems.
Ecologists may study populations, communities, ecosystems, or the biosphere. They use a variety of methods, including observations, experiments, and models, to understand ecological phenomena.


Evolution
Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations. Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth. These processes include natural selection, common descent, and speciation.
The theory of evolution by natural selection, first formulated by Charles Darwin, is widely accepted as the central explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. It posits that species evolve over time through a process of natural selection, where traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in successive generations.


Conclusion
Biology is a vast and diverse field that encompasses the study of all aspects of life. From the smallest microorganisms to the largest ecosystems, biology helps us understand the complex interactions that make life possible. As our knowledge of biology expands, so too does our ability to develop new medicines, conserve biodiversity, and understand our place in the natural world.
