Tissue (biology)
Overview
Tissue, in biological terms, is a group of cells that perform a similar function and are similar in structure. It is the material or substance of which animals or plants are formed. Tissues combine to form organs, which then form organ systems. The study of tissues is known as histology.
Types of Tissues
There are four basic types of tissues in the body of all animals, including humans. These are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
Epithelial Tissue
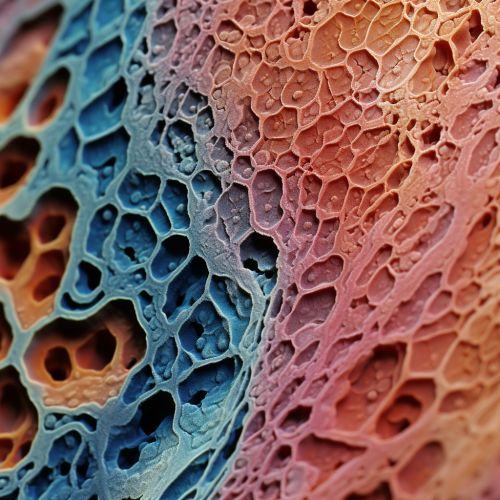

Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissues are the most abundant and widely distributed of the primary tissues. Connective tissues perform a variety of functions including support and protection. The following types are found in the human body: loose connective tissue (areolar), adipose tissue, fibrous connective tissue (dense), elastic connective tissue, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissues, as the name suggests, are responsible for movement in the body. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Each of these has a unique structure and a specific role in the body.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissues are responsible for transmitting and receiving signals in the body. They are found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells: neurons and neuroglia.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Tissue repair and regeneration is a complex process that involves the replacement of damaged or dead cells. This process is crucial for the survival of an organism, as it helps to maintain the integrity of tissues and organs. The ability of a tissue to regenerate depends on its cellular composition. Some tissues, like epithelial and connective tissues, have a high regenerative capacity. Others, like nervous and muscle tissues, have a limited ability to regenerate.
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a multidisciplinary field that aims to develop functional tissues and organs in the laboratory to replace or repair damaged tissues in the body. This field combines principles from biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine to create and cultivate tissues.
Tissue Culture
Tissue culture is a technique used in biology to maintain or grow tissue cells in an artificial environment conducive to their growth. This technique is used in a variety of applications, including research, clinical treatment, and industry.
