The Role of Geostatistics in Predicting Landslides
Introduction
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics that deals with spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. It has been widely used in a variety of fields, such as mineral resource estimation, hydrocarbon exploration, environmental science, and geotechnical engineering. One of the significant applications of geostatistics is in predicting landslides, a natural disaster that causes significant loss of life and property worldwide.


Geostatistics: An Overview
Geostatistics originated from the mining and petroleum industries, where it was used to predict the likelihood of finding valuable resources. The discipline has since expanded to include a wide range of applications, including the prediction of natural disasters such as landslides. It uses statistical methods to analyze spatially correlated data, with the aim of predicting values at unobserved locations.


Role of Geostatistics in Landslide Prediction
Geostatistics plays a crucial role in landslide prediction by providing a statistical approach to the spatial analysis of landslide susceptibility. It allows for the analysis of various factors that contribute to landslides, such as slope, aspect, curvature, lithology, land use, and rainfall, among others.
Data Collection and Analysis
The first step in geostatistical landslide prediction is data collection. This involves gathering data on the various factors that contribute to landslides. Once the data has been collected, it is then analyzed using geostatistical methods to identify patterns and correlations.


Landslide Susceptibility Mapping
One of the primary applications of geostatistics in landslide prediction is in the creation of landslide susceptibility maps. These maps provide a visual representation of the areas that are most likely to experience landslides, based on the analysis of the contributing factors.
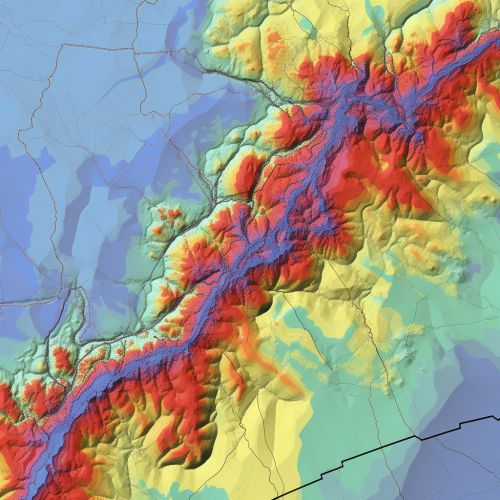
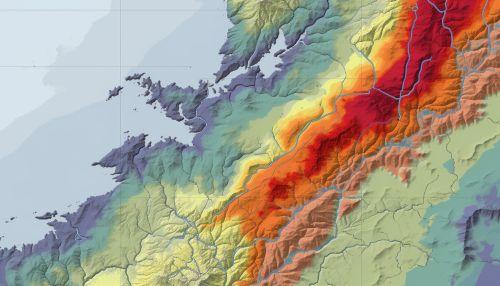
Prediction and Risk Assessment
Once the landslide susceptibility map has been created, it can be used to predict future landslides and assess the risk associated with them. This information can then be used to inform land use planning and disaster management strategies.


Challenges and Limitations
While geostatistics provides a powerful tool for landslide prediction, it is not without its challenges and limitations. These include the quality and availability of data, the complexity of the statistical methods used, and the inherent uncertainty associated with predicting natural disasters.
Conclusion
Despite these challenges, the role of geostatistics in predicting landslides is undeniable. It provides a scientific and systematic approach to understanding and predicting landslides, thereby contributing to the safety and well-being of communities at risk.
