Root endophyte
Introduction
Root endophytes are fungal or bacterial organisms that live within the tissues of a plant's root system without causing apparent harm to the host. They form a symbiotic relationship with the plant, offering benefits such as enhanced nutrient uptake, disease resistance, and stress tolerance. The study of root endophytes is a specialized field within microbiology and plant pathology, with implications for agriculture, ecology, and biotechnology.
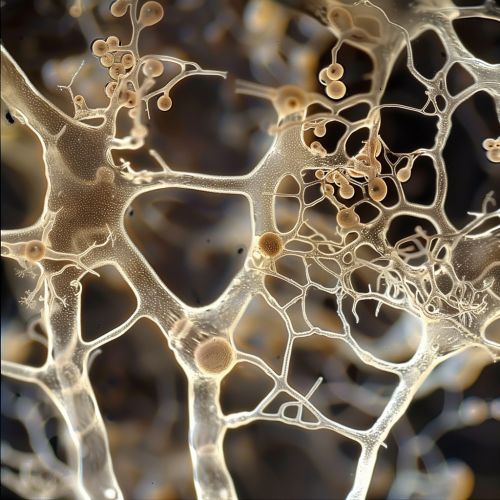

Biology of Root Endophytes
Root endophytes are diverse in their taxonomy, with representatives from various fungal and bacterial phyla. They colonize the intercellular spaces of root tissues, and in some cases, they can also penetrate root cells. The colonization process involves a complex interplay of chemical signals between the endophyte and the host plant. Some root endophytes are able to form structures called mycorrhizae, which increase the root surface area and facilitate nutrient exchange.
Ecological Role
Root endophytes play a crucial role in plant health and productivity. They assist in nutrient acquisition, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, from the soil. Some endophytes can also produce plant growth-promoting hormones, enhancing plant development. Furthermore, they can protect the plant against pathogens by producing antimicrobial compounds or by outcompeting pathogenic microorganisms for resources.
Agricultural and Biotechnological Applications
The use of root endophytes in agriculture and biotechnology is a growing field of research. By enhancing plant growth and disease resistance, endophytes can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices. They can also be used in bioremediation, a process that uses living organisms to clean up polluted environments. In addition, endophytes are a potential source of novel bioactive compounds for pharmaceutical and industrial applications.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their potential benefits, the use of root endophytes in practical applications faces several challenges. These include the difficulty in isolating and culturing endophytes, the variability in endophyte-host interactions, and the potential risks associated with introducing non-native endophytes into the environment. Future research aims to overcome these challenges and to further our understanding of endophyte biology and ecology.
