Mycorrhiza
Introduction
Mycorrhizae are symbiotic relationships that form between fungi and plants. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungi in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in soil biology and soil chemistry.
Types of Mycorrhizae
There are several types of mycorrhizae, including ectomycorrhizae, endomycorrhizae, and ericoid mycorrhizae.
Ectomycorrhizae
Ectomycorrhizal fungi form a sheath of tissue, known as a mantle, around the root tips of host plants. The hyphae of these fungi can penetrate the outer cells of the plant roots, forming a network of intercellular hyphae.
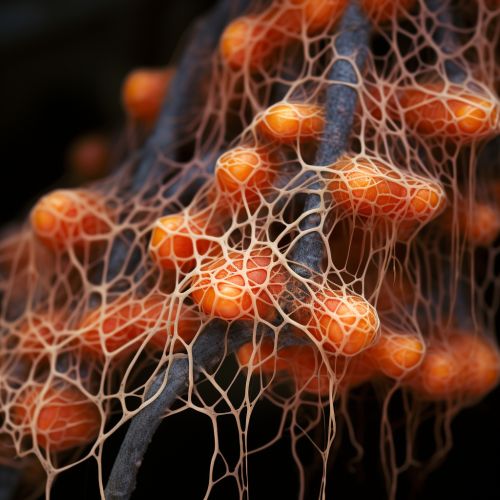
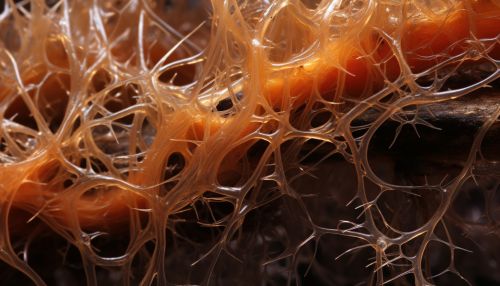
Endomycorrhizae
Endomycorrhizal fungi, also known as arbuscular mycorrhizae, penetrate the cortical cells of the plant roots, forming arbuscules, which are highly branched structures that are involved in nutrient exchange between the plant and the fungus.
Ericoid Mycorrhizae
Ericoid mycorrhizal fungi form associations with plants in the family Ericaceae, which includes species such as heathers and blueberries. These fungi form a dense network of hyphae in the root cortex, and also penetrate the root cells.
Function of Mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae play a crucial role in nutrient uptake in plants, aiding in the absorption of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and zinc. They also play a role in plant growth and development, and can influence plant community structure.
Nutrient Uptake
Mycorrhizal fungi form extensive networks of hyphae in the soil, which can access and absorb nutrients from areas beyond the reach of the plant roots. The fungi can then transport these nutrients back to the plant, aiding in nutrient uptake.
Plant Growth and Development
Mycorrhizal fungi can also influence plant growth and development. For example, the presence of mycorrhizal fungi can enhance root development, leading to increased root biomass and improved plant growth.
Influence on Plant Community Structure
Mycorrhizal fungi can also influence plant community structure. For example, in ecosystems where mycorrhizal fungi are abundant, plant species that are able to form mycorrhizal associations may be more successful, leading to changes in plant community composition.
Mycorrhizae and Soil Health
Mycorrhizal fungi play a key role in maintaining soil health. They contribute to soil structure, aid in nutrient cycling, and can help to mitigate soil erosion.
Soil Structure
Mycorrhizal fungi contribute to soil structure through the formation of hyphal networks, which can bind soil particles together, creating stable aggregates.
Nutrient Cycling
Mycorrhizal fungi play a key role in nutrient cycling in the soil. They can aid in the decomposition of organic matter, releasing nutrients into the soil. They can also immobilize nutrients, preventing them from being leached away from the soil.
Mitigation of Soil Erosion
Mycorrhizal fungi can also help to mitigate soil erosion. The hyphal networks of these fungi can help to bind soil particles together, reducing soil erosion by water and wind.
Conclusion
Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with plants, playing crucial roles in nutrient uptake, plant growth and development, and soil health. Understanding the role of these fungi in ecosystems can provide insights into plant community structure, nutrient cycling, and soil erosion.
