Role of Geoinformatics in Water Resource Management
Introduction
Geoinformatics, also known as geospatial informatics or geomatics, is the science and the technology which develops and uses information science infrastructure to address the problems of geography, geosciences and related branches of engineering. It is the practical application of geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), photogrammetry, geodesy, geography and related forms of earth mapping. This discipline plays a significant role in water resource management, which is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources.


Role of Geoinformatics in Water Resource Management
Water resource management is a complex field that involves the balancing of water resource use and conservation, while considering factors such as climate change, population growth, and economic development. Geoinformatics provides the tools and methodologies necessary for effective water resource management.
Data Collection and Analysis
Geoinformatics plays a crucial role in the collection, storage, analysis, and dissemination of spatial data related to water resources. This includes data on water quality, quantity, distribution, and usage. For instance, remote sensing technologies, such as satellites and drones, can collect data on precipitation, evaporation, and transpiration rates, as well as soil moisture levels and vegetation cover. These data can then be analyzed using GIS to identify patterns, trends, and relationships, which can inform water resource management decisions.


Water Resource Planning and Management
GIS and other geoinformatics tools are essential for water resource planning and management. They can be used to create detailed maps and models of water systems, which can help in the planning of water supply and distribution networks, irrigation systems, and flood control measures. For example, a GIS can be used to model the impact of different water management scenarios, such as the construction of a new dam or the implementation of water conservation measures. This can help decision-makers to make informed choices and to anticipate and mitigate potential negative impacts.
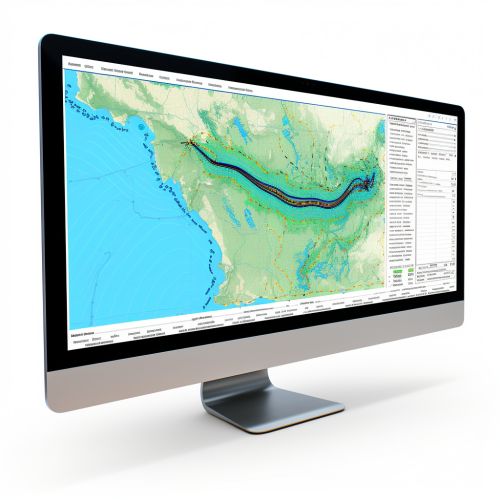

Monitoring and Evaluation
Geoinformatics is also crucial for the monitoring and evaluation of water resources. Remote sensing technologies can provide real-time data on water levels, flow rates, and quality, which can be used to monitor the status of water resources and to detect any changes or anomalies. This can help to identify issues such as water scarcity, pollution, or overuse, and to take appropriate action. Furthermore, GIS can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of water management strategies and interventions, by comparing pre- and post-intervention data.


Challenges and Opportunities
While geoinformatics offers many opportunities for water resource management, it also presents several challenges. These include the high cost of geoinformatics technologies, the need for specialized skills and training, and issues related to data quality, availability, and interoperability. However, advances in technology and the increasing availability of open-source geoinformatics tools are helping to overcome these challenges.


Conclusion
In conclusion, geoinformatics plays a vital role in water resource management, by providing the tools and methodologies necessary for data collection and analysis, planning and management, and monitoring and evaluation. Despite the challenges, the opportunities offered by geoinformatics are immense and are likely to increase with advances in technology.
