Population Growth
Introduction
Population growth refers to the increase in the number of individuals in a population. It is a fundamental concept in demography, the scientific study of populations. The rate at which a population grows can have significant impacts on economic, sociological, and ecological factors within a society or ecosystem.


Factors Influencing Population Growth
Population growth is influenced by a variety of factors, including birth rates, death rates, and migration. These factors are often influenced by broader social, economic, and environmental factors.
Birth Rates
The birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people per year. High birth rates can lead to rapid population growth, particularly if death rates are low. Factors influencing birth rates include cultural attitudes towards family size, availability of contraception, and government policies.
Death Rates
The death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people per year. Lower death rates can contribute to population growth. Factors influencing death rates include healthcare quality, nutrition, and environmental conditions.
Migration
Migration, the movement of people from one place to another, can also influence population growth. Immigration can increase a population, while emigration can decrease it. Factors influencing migration include economic opportunities, political stability, and environmental conditions.


Population Growth Models
Demographers use various models to predict population growth. These models take into account factors such as birth rates, death rates, and migration.
Exponential Growth Model
The exponential growth model assumes that a population will grow at a constant rate. This model is often used to describe populations with unlimited resources.
Logistic Growth Model
The logistic growth model assumes that a population's growth rate will decrease as the population size approaches its carrying capacity. This model is often used to describe populations with limited resources.
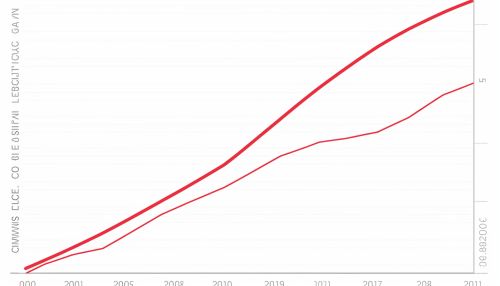
Impacts of Population Growth
Population growth can have significant impacts on society and the environment.
Economic Impacts
Economic impacts of population growth can be both positive and negative. On the positive side, a growing population can lead to economic growth as more people contribute to the economy. On the negative side, rapid population growth can strain resources and infrastructure.
Sociological Impacts
Sociological impacts of population growth include changes in social structures and institutions. Rapid population growth can lead to urbanization, changes in family structures, and shifts in cultural norms.
Ecological Impacts
Ecological impacts of population growth include increased resource consumption and environmental degradation. Rapid population growth can lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and climate change.


Population Control Measures
Various measures can be taken to control population growth. These include family planning programs, education, and economic development.
Family Planning
Family planning programs can help control population growth by providing access to contraception and reproductive health services.
Education
Education, particularly for women, can help control population growth. Educated women tend to have fewer children and have them later in life.
Economic Development
Economic development can also help control population growth. As countries develop economically, birth rates often decline.


Conclusion
Population growth is a complex issue with significant impacts on society and the environment. Understanding the factors that influence population growth and the measures that can be taken to control it is crucial for sustainable development.
