Electroencephalogram
Overview
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that records electrical activity in the brain. The brain's electrical activity is detected by electrodes, or sensors, placed on the patient's scalp and transmitted to a machine that records the activity. EEG is a fundamental tool in the field of neurology, and it has a wide range of applications in clinical practice and research.

History
The concept of EEG was first introduced by a British physician, Richard Caton, in the late 19th century. However, the first human EEG recording was made by a German psychiatrist, Hans Berger, in 1924. Berger's work laid the foundation for the development of EEG as a clinical and research tool.
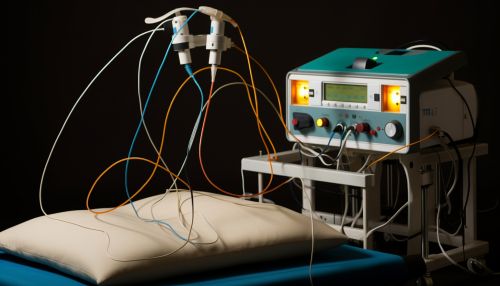
Procedure
The EEG procedure involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect electrical activity in the brain. The electrodes are connected to an EEG machine, which amplifies the signals and records them on a computer. The recorded data is then analyzed by a neurologist or a trained technician.
Applications
EEG has a wide range of applications in both clinical practice and research. In clinical practice, EEG is used to diagnose and monitor various neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and encephalopathy. In research, EEG is used to study brain function and to develop new treatments for neurological disorders.
Limitations
Despite its wide range of applications, EEG has several limitations. The main limitation of EEG is its poor spatial resolution, which means it cannot accurately pinpoint the location of brain activity. Additionally, EEG cannot detect electrical activity deep within the brain.
Future Directions
Advancements in technology and computational methods are expected to overcome some of the limitations of EEG. For example, high-density EEG systems and advanced signal processing techniques are being developed to improve the spatial resolution of EEG.
