Echocardiogram
Definition
An Echocardiogram is a diagnostic test that uses ultrasound waves to produce images of the heart. This non-invasive procedure allows medical professionals to observe the heart's structure and function, providing valuable information about the size, shape, and movement of the heart and its component parts.
Types of Echocardiograms
There are several types of echocardiograms, each with its own specific uses and benefits.
Transthoracic Echocardiogram
The most common type of echocardiogram is the Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE), which involves placing an ultrasound probe on the chest wall to obtain images of the heart.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram
A Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) involves inserting a specialized probe into the esophagus. This allows for more detailed images as the esophagus is closer to the heart, and there are fewer intervening structures.
Stress Echocardiogram
A Stress Echocardiogram is performed while the patient is exercising or under pharmacologic stress. This test can reveal how the heart responds to stress and can be useful in diagnosing coronary artery disease.
Doppler Echocardiogram
A Doppler Echocardiogram uses Doppler ultrasound to measure the speed and direction of blood flow within the heart. This can help to identify abnormal blood flow patterns and evaluate heart valve function.
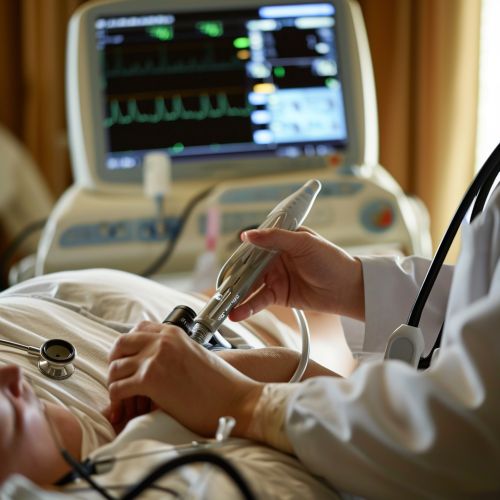
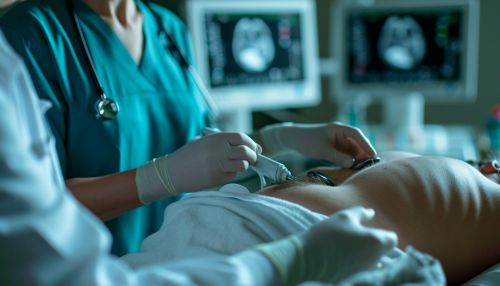
Procedure
The procedure for an echocardiogram varies depending on the type of test being performed. However, all echocardiograms involve the use of an ultrasound machine and a transducer, which emits and receives the ultrasound waves.
Preparation
Before the echocardiogram, the patient may be asked to remove clothing from the waist up and put on a hospital gown. The patient is then positioned on an examination table or bed.
Conducting the Echocardiogram
During the procedure, the sonographer applies a gel to the skin over the area to be examined. This gel helps to conduct the ultrasound waves. The sonographer then places the transducer against the skin and moves it around to obtain images of the heart from different angles.
Interpretation
The images obtained from an echocardiogram are interpreted by a cardiologist or other medical professional with training in echocardiography. They will evaluate the size, shape, and movement of the heart and its components, as well as the blood flow through the heart. The results of an echocardiogram can provide valuable information about a variety of heart conditions, including heart disease, heart failure, and heart valve disorders.
Risks and Limitations
Echocardiograms are generally safe procedures with minimal risks. However, there are some limitations to the test. For example, the quality of the images obtained can be affected by factors such as body size, body habitus, and lung disease. In addition, while echocardiograms can provide valuable information about the heart, they cannot provide a comprehensive assessment of the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle.
Applications
Echocardiograms are used in a variety of clinical settings and for a range of purposes. These include diagnosing and monitoring heart disease, evaluating symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath, assessing heart function before and after heart surgery, and monitoring the effects of certain medications on the heart.
