Brain Tumor
Introduction
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain. There are many different types of brain tumors. Some are benign, or non-cancerous, while others are malignant, or cancerous. Brain tumors can begin in the brain (primary brain tumors), or they can begin in other parts of the body and spread to the brain (secondary, or metastatic, brain tumors). The exact cause of primary brain tumors is not well understood, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
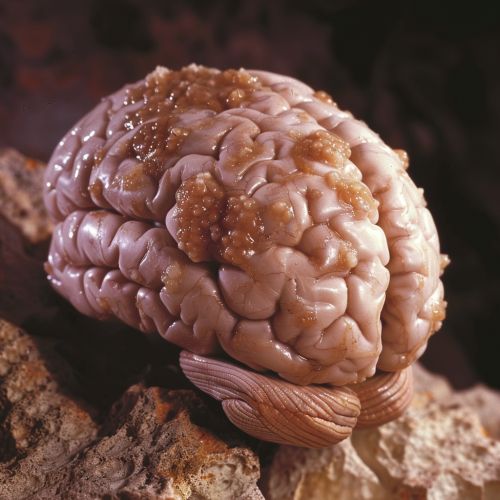
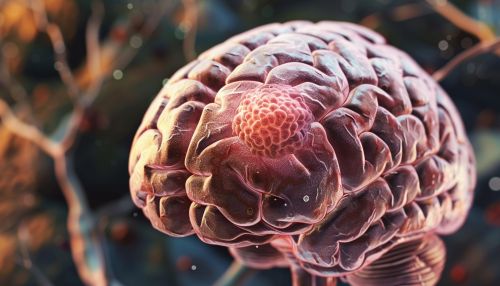
Types of Brain Tumors
Brain tumors are classified based on the type of cell where the tumor begins, the location of the tumor, and its rate of growth. The most common types of primary brain tumors in adults are gliomas and meningiomas. Gliomas begin in the glial cells, which provide support and protection for the neurons. Meningiomas, on the other hand, begin in the meninges, the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary greatly and depend on the tumor's size, location, and rate of growth. Common symptoms may include new or changing seizures, persistent headaches, vision problems, speech difficulties, loss of balance, and changes in behavior or personality. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than brain tumors, so it is essential to seek medical advice if any of these symptoms are experienced.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a brain tumor usually involves a neurological examination, imaging tests such as MRI, and in some cases, a biopsy. A neurological examination may include, among other things, a vision test, hearing test, balance test, coordination test, and reflex test. If a tumor is suspected, an MRI is often used to confirm the diagnosis and provide detailed information about the tumor.
Treatment
Treatment options for brain tumors depend on the type of tumor, its size and location, and the patient's overall health. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, or a combination of these. In some cases, if the tumor is small and not causing any symptoms, a wait-and-see approach may be recommended.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a person with a brain tumor can vary greatly depending on the type of tumor, its location, its size, and the person's overall health. Some brain tumors are benign and can be successfully removed with surgery, while others are malignant and may require additional treatments such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy. The survival rate for people with malignant brain tumors varies, but advancements in treatment have led to improved survival rates in recent years.
