Wireframe Model
Introduction
A wireframe model is a visual representation of a three-dimensional (3D) object used in 3D computer graphics. It is created by specifying each edge of the physical object where two mathematically continuous smooth surfaces meet, or by connecting an object's constituent vertices using straight lines or curves. The object is projected into screen space and rendered by drawing lines at the location of each edge.
History
The concept of wireframe modeling originated in the 1960s with the advent of CAD systems, where it was used for the representation and design of complex industrial parts. The term "wireframe" comes from designers' use of metal wires to represent the three-dimensional shape of solid objects.

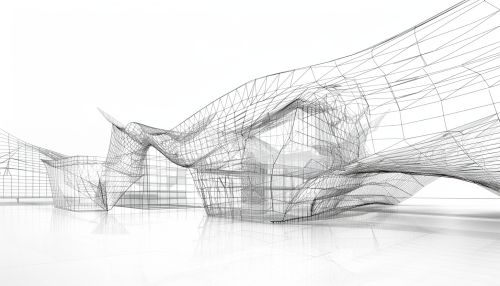
Wireframe Modeling Techniques
Wireframe modeling techniques can be divided into two main categories: object representation and visualization.
Object Representation
In object representation, the wireframe model is used to represent the geometric structure of a 3D object. This is done by defining the object's vertices and the edges connecting them. The edges are typically represented as straight lines, but can also be represented as curves in some cases.
Visualization
In visualization, the wireframe model is used to create a visual representation of the object. This is done by projecting the object onto a two-dimensional screen and drawing lines at the location of each edge. The lines are typically drawn in a way that simulates the appearance of a solid object, but can also be drawn in a way that emphasizes the object's structure.
Applications
Wireframe models are used in a wide range of applications, from engineering and architecture to entertainment and art.
Engineering and Architecture
In engineering and architecture, wireframe models are used to design and visualize complex structures. They allow engineers and architects to examine the structure's shape and size, identify potential problems, and make necessary adjustments before construction begins.
Entertainment
In the entertainment industry, wireframe models are used in the production of video games and movies. They are used to create 3D characters, objects, and environments, which are then rendered using various techniques to create the final visual effects.
Art
In art, wireframe models are used to create 3D sculptures and installations. They provide a unique aesthetic that combines the precision of digital design with the physicality of traditional sculpture.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any modeling technique, wireframe modeling has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
One of the main advantages of wireframe modeling is its simplicity. It allows designers to focus on the essential structure of an object, without getting distracted by its surface details. This can be particularly useful in the early stages of design, when the overall shape and proportions of the object are more important than its detailed appearance.
Another advantage of wireframe modeling is its flexibility. It allows designers to easily make changes to the object's structure, without having to modify its surface details. This can be particularly useful in the later stages of design, when minor adjustments can have a significant impact on the object's performance or aesthetics.
Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of wireframe modeling is its lack of realism. It does not provide a realistic representation of an object's appearance, which can make it difficult to evaluate the object's visual impact. This can be particularly problematic in fields like product design and architecture, where the object's appearance is often as important as its function.
Another disadvantage of wireframe modeling is its lack of precision. It does not provide a precise representation of an object's surface, which can make it difficult to evaluate the object's physical properties. This can be particularly problematic in fields like engineering and medicine, where the object's physical properties can have a significant impact on its performance or safety.
