Water Harvesting
Introduction
Water harvesting is a technique used to gather and store rainwater for reuse before it reaches the aquifer. It uses principles of hydrology and engineering to manage the flow and storage of water. Water harvesting systems can be simple to construct from inexpensive local materials, and are potentially successful in most habitable locations.


History
The practice of water harvesting is believed to have originated in the arid and semi-arid regions of the world, where water scarcity has been a major issue for centuries. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and India developed sophisticated water harvesting systems, including wells, dams, and reservoirs, to collect and store rainwater for irrigation and other uses.
Types of Water Harvesting
There are two main types of water harvesting: surface water harvesting and rooftop water harvesting.
Surface Water Harvesting
Surface water harvesting involves the collection of rainwater from surfaces such as ponds, lakes, and reservoirs. This method is often used in rural areas where large amounts of land are available for the construction of water storage facilities.


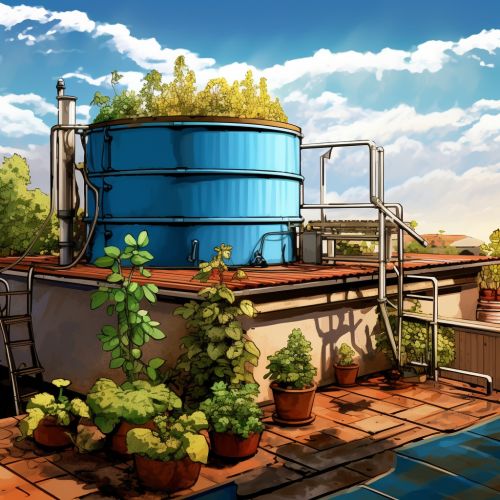
Rooftop Water Harvesting
Rooftop water harvesting involves the collection of rainwater from roof surfaces, typically using gutters and downspouts to direct the water into storage tanks. This method is often used in urban areas where space is limited.


Benefits of Water Harvesting
Water harvesting provides numerous benefits, including the provision of a sustainable water supply, reduction of water bills, and minimization of the impact of water scarcity. It also aids in reducing soil erosion and flooding by reducing runoff.
Design and Construction of Water Harvesting Systems
The design and construction of a water harvesting system depends on several factors, including the local climate, the size and type of the catchment area, and the intended use of the harvested water. The system typically includes a catchment area, a conveyance system, a storage facility, and a distribution system.
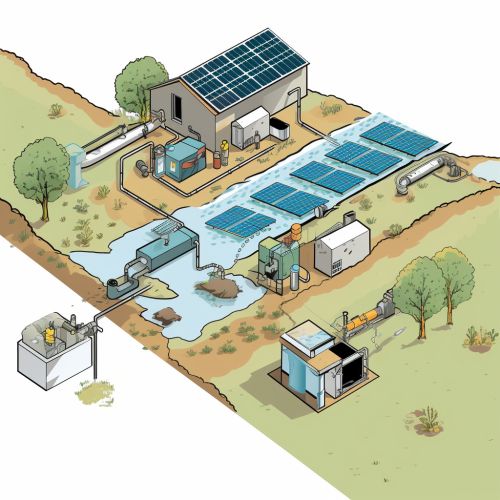

Maintenance of Water Harvesting Systems
Regular maintenance of water harvesting systems is essential to ensure their long-term functionality and efficiency. This includes cleaning the catchment area and conveyance system, inspecting and repairing the storage facility, and checking the quality of the harvested water.


Challenges and Solutions
Despite the numerous benefits, water harvesting also presents several challenges, including the initial cost of the system, potential water quality issues, and regulatory constraints. However, these challenges can be overcome through careful planning, appropriate design, regular maintenance, and the use of appropriate water treatment methods.
Future of Water Harvesting
The future of water harvesting looks promising, with advances in technology and growing awareness of the importance of water conservation. With the increasing threat of water scarcity due to climate change, the need for sustainable water management practices such as water harvesting is more important than ever.
