Thermodilution
Introduction
Thermodilution is a technique used in the medical field to measure cardiac output, the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, specifically by the left or right ventricle in the time period of one minute. This method is based on the principles of the indicator dilution technique, which involves the injection of a thermal indicator into the bloodstream and the subsequent measurement of temperature changes in the blood to determine cardiac output.
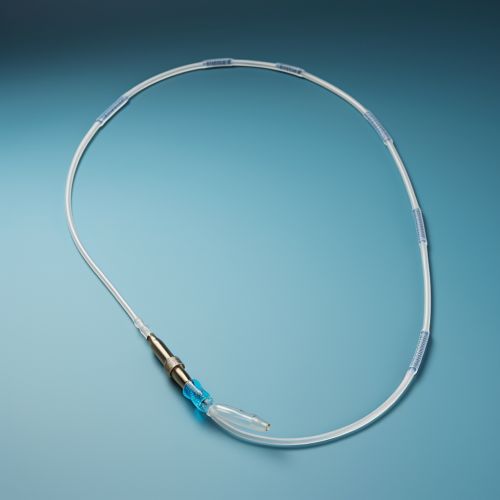
Principles of Thermodilution
The thermodilution method is a type of indicator dilution method. The indicator dilution method involves the injection of an indicator, in this case a thermal indicator, into the bloodstream. The change in blood temperature is then measured downstream, and this change is used to calculate cardiac output.
Thermal Indicator
In the thermodilution method, the thermal indicator is usually a bolus of saline solution at a known temperature, typically cooler than the blood. When this bolus is injected into the bloodstream, it causes a change in blood temperature. This change is detected by a thermistor located at the tip of a Swan-Ganz catheter, which is positioned in the pulmonary artery.
Measurement and Calculation
The thermistor measures the change in blood temperature over time, producing a thermodilution curve. The area under this curve is inversely proportional to the cardiac output. Thus, by analyzing the thermodilution curve, the cardiac output can be calculated.
Clinical Applications
Thermodilution is commonly used in critical care medicine to monitor cardiac output in critically ill patients. It is also used in cardiology for the diagnosis and management of various heart conditions.
Critical Care Medicine
In critical care medicine, monitoring of cardiac output is essential for the management of patients with shock, severe sepsis, and other critical conditions. Thermodilution, performed using a Swan-Ganz catheter, provides a reliable and accurate measure of cardiac output, which can guide fluid and drug therapy in these patients.
Cardiology
In cardiology, thermodilution is used to assess cardiac function in patients with heart failure and other heart conditions. It can provide valuable information about the severity of heart failure, the effectiveness of treatment, and the prognosis of the patient.
Advantages and Limitations
Like any medical procedure, thermodilution has its advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help clinicians make the best use of this technique.
Advantages
Thermodilution is considered the gold standard for measuring cardiac output in critically ill patients. It is relatively easy to perform and provides accurate and reliable results. Moreover, the Swan-Ganz catheter used in thermodilution can also be used to measure other important parameters such as pulmonary artery pressure and central venous pressure.
Limitations
Despite its advantages, thermodilution has some limitations. It is an invasive procedure and thus carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and pneumothorax. It also requires the use of a Swan-Ganz catheter, which is a complex device and requires expertise to use correctly. Furthermore, the thermodilution method may not be accurate in patients with certain conditions such as tricuspid regurgitation and intracardiac shunts.
