Thermal Management Techniques
Introduction
Thermal management techniques are essential in a variety of fields, including electronics, automotive engineering, and aerospace engineering. These techniques are used to control the temperature of systems and components, ensuring that they operate within their optimal temperature range. This article will delve into the various thermal management techniques used in these fields, providing a comprehensive and detailed overview of each technique.
Thermal Management in Electronics
In the field of electronics, thermal management is crucial to ensure the longevity and reliability of electronic components. As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, the heat generated by these devices increases. This heat must be effectively managed to prevent damage to the components and to ensure the device operates efficiently.
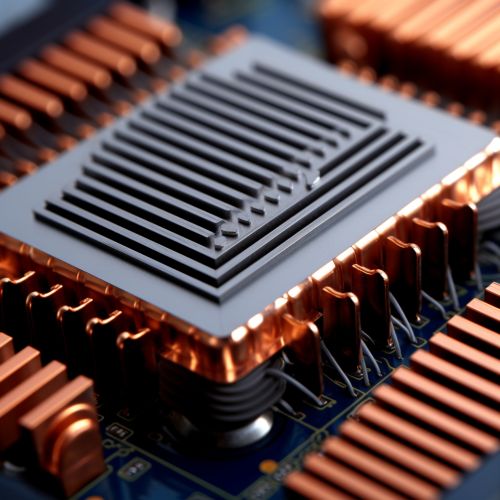
Heat Sinks
One of the most common thermal management techniques in electronics is the use of heat sinks. Heat sinks are devices that absorb and dissipate heat from electronic components. They work by increasing the surface area in contact with the cooling medium, such as air. The design of a heat sink can greatly affect its efficiency. Factors such as material, size, shape, and fin arrangement can all influence the performance of a heat sink.

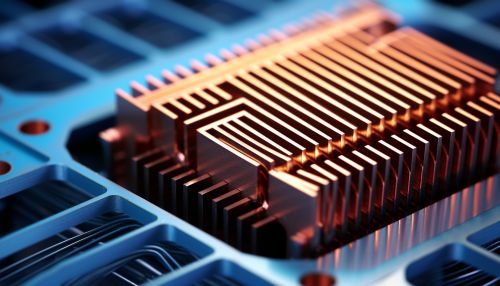
Thermal Interface Materials
Another important aspect of thermal management in electronics is the use of thermal interface materials (TIMs). TIMs are materials that are applied between the heat source (such as a microprocessor) and the heat sink. They serve to fill the microscopic air gaps between the two surfaces, improving the thermal conductivity and heat transfer efficiency.
Liquid Cooling
In high-performance electronic systems, such as servers and gaming computers, liquid cooling systems are often used. These systems use a liquid coolant to absorb heat from the components and then dissipate it through a radiator. Liquid cooling systems can be more efficient than air cooling systems, but they are also more complex and can be more expensive to implement.
Thermal Management in Automotive Engineering
In the automotive industry, thermal management techniques are used to control the temperature of various components, including the engine, transmission, and battery in electric vehicles.
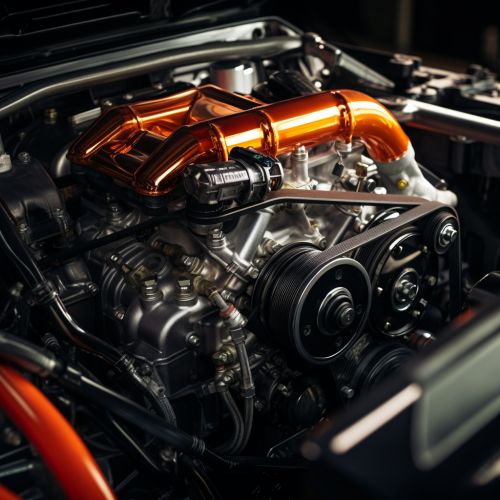
Engine Cooling
The most well-known thermal management technique in automotive engineering is engine cooling. This involves the use of a coolant (usually a mixture of water and antifreeze) to absorb heat from the engine and then dissipate it through a radiator. The cooling system also includes a thermostat to control the flow of coolant, and a fan to increase airflow through the radiator when needed.


Transmission Cooling
In addition to engine cooling, transmission cooling is also important in vehicles. The transmission generates heat as it transfers power from the engine to the wheels. This heat can be managed through the use of a transmission cooler, which is often integrated with the radiator.
Battery Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles
In electric vehicles, battery thermal management is crucial. The battery pack can generate significant heat during operation, especially during fast charging or high-power discharge. This heat must be managed to prevent damage to the battery cells and to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the battery pack. Techniques for battery thermal management can include air cooling, liquid cooling, and phase change materials.
Thermal Management in Aerospace Engineering
In the field of aerospace engineering, thermal management is a critical issue. The extreme temperatures encountered in space and during re-entry to the Earth's atmosphere require sophisticated thermal management techniques.
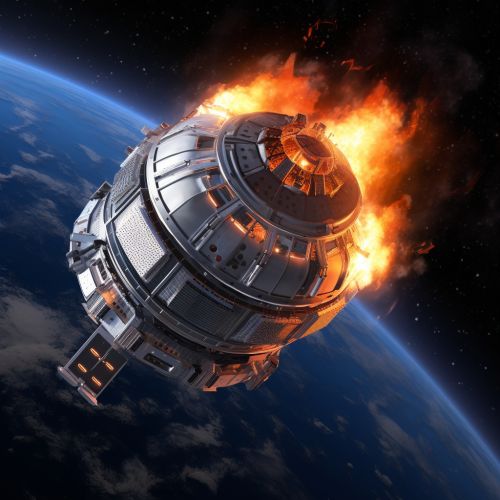
Thermal Protection Systems
One of the key thermal management techniques in aerospace engineering is the use of thermal protection systems (TPS). These systems are designed to protect spacecraft and their occupants from the extreme heat generated during re-entry. The TPS typically includes a heat shield made of ablative material that burns off and dissipates heat as the spacecraft re-enters the atmosphere.


Active Thermal Control Systems
In addition to passive thermal protection systems, spacecraft also use active thermal control systems (ATCS). These systems use a variety of techniques to manage the temperature of the spacecraft, including heat pipes, radiators, and thermal storage units.
