Supercomputer
Definition and Overview
A supercomputer is a type of computer system that possesses extreme computational capabilities. These machines are designed to perform complex simulations, data analysis, and other tasks that require a high level of processing power. Supercomputers are often used in scientific research, weather forecasting, and other fields where large amounts of data need to be processed quickly and accurately.


History
The concept of the supercomputer dates back to the 1960s, when the first systems were developed by companies such as IBM and Control Data Corporation. These early supercomputers were large, expensive, and required specialized knowledge to operate. However, they provided unprecedented processing power, enabling researchers to tackle problems that were previously thought to be unsolvable.
Over the years, supercomputers have evolved significantly. The advent of parallel computing in the 1980s allowed for the development of supercomputers that could perform many calculations simultaneously, dramatically increasing their processing power. Today's supercomputers are capable of performing quadrillions of calculations per second, and are used in a wide range of applications, from climate modeling to drug discovery.
Architecture
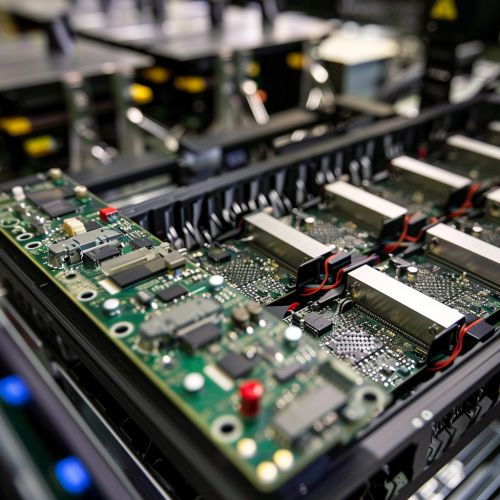
Supercomputers are typically composed of thousands of central processing units (CPUs) or graphics processing units (GPUs), which are interconnected to form a massive parallel processing system. This architecture allows supercomputers to perform a large number of calculations simultaneously, making them ideal for tasks that require a high level of computational power.
In addition to CPUs and GPUs, supercomputers also often include other specialized hardware, such as field-programming gate arrays (FPGAs) and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). These components can be programmed to perform specific tasks, further enhancing the supercomputer's processing capabilities.


Applications
Supercomputers are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Scientific research: Supercomputers are used to simulate complex physical phenomena, such as the behavior of subatomic particles or the evolution of galaxies. These simulations can provide valuable insights into the nature of the universe and help guide future research.
- Weather forecasting: Supercomputers are used to analyze large amounts of meteorological data and generate accurate weather forecasts. These forecasts can help predict severe weather events and aid in disaster planning.
- Drug discovery: Supercomputers can simulate the interactions between molecules, helping researchers identify potential new drugs. This can significantly speed up the drug discovery process and potentially lead to new treatments for diseases.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Supercomputers are used to train AI models, which require a large amount of computational power. This can lead to advancements in fields such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
Future Trends
The field of supercomputing continues to evolve, with new technologies and architectures being developed to increase processing power and efficiency. One of the most promising trends is the development of quantum computers, which could potentially outperform traditional supercomputers by many orders of magnitude. However, quantum computing is still in its early stages, and it may be several years before quantum supercomputers become a reality.