Spacecraft Design
Introduction
Spacecraft design is a complex and specialized field of engineering that focuses on the development of systems for use in outer space. The process involves a detailed understanding of a variety of disciplines, including astrodynamics, materials science, thermodynamics, and propulsion systems. This article delves into the intricacies of spacecraft design, providing an in-depth look at the various aspects involved in creating a functional and efficient spacecraft.
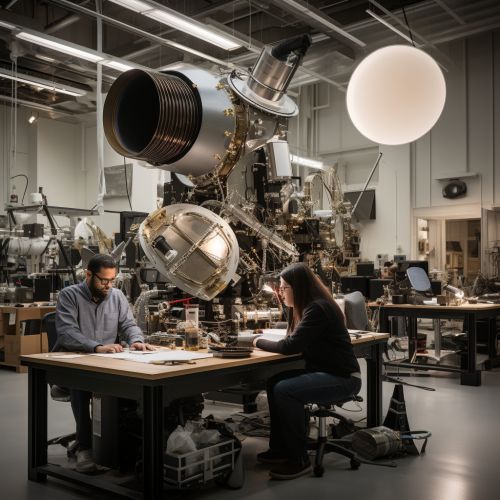


History of Spacecraft Design
The history of spacecraft design is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1957, marking the beginning of the space age. Since then, spacecraft design has evolved significantly, with advancements in technology enabling the creation of more sophisticated and capable spacecraft.

Design Considerations
Designing a spacecraft requires careful consideration of a multitude of factors. These include the mission objectives, the operational environment, available technologies, and budget constraints. The spacecraft must be designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space, including extreme temperatures, radiation, and the vacuum of space. Additionally, the spacecraft must be able to carry out its mission effectively, whether it be scientific research, communication, navigation, or human spaceflight.

Mission Objectives
The mission objectives play a crucial role in the design of a spacecraft. These objectives define the spacecraft's purpose and determine its key design features. For example, a spacecraft designed for a rover mission to Mars would require a different design than a spacecraft intended for a comet observation mission.
Operational Environment
The operational environment of a spacecraft is another critical factor in its design. Spacecraft are exposed to a variety of harsh conditions in space, including extreme temperatures, high levels of radiation, and microgravity. These conditions necessitate the use of specialized materials and design techniques to ensure the spacecraft's functionality and longevity.
Available Technologies
The available technologies at the time of design also influence the design of a spacecraft. Advances in technology can enable new capabilities and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of spacecraft. For example, advancements in propulsion technology can allow for faster and more efficient travel, while improvements in communication technology can enhance the ability of a spacecraft to transmit data back to Earth.
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints often play a significant role in the design of a spacecraft. The cost of designing, building, and launching a spacecraft can be astronomical, and budget considerations can limit the scope and capabilities of a spacecraft. As such, spacecraft designers must strive to maximize the spacecraft's capabilities while minimizing its cost.
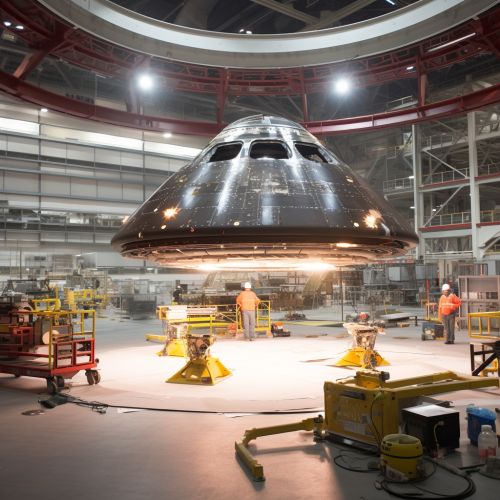


Design Process
The design process for a spacecraft involves several stages, from initial concept development to detailed design and testing. This process requires a multidisciplinary team of engineers and scientists, who work together to create a spacecraft that meets its mission objectives and can withstand the harsh conditions of space.


Concept Development
The first stage in the design process is concept development. During this stage, the mission objectives are defined, and a preliminary design for the spacecraft is developed. This involves determining the spacecraft's size, shape, and configuration, as well as its key systems and components.
Detailed Design
Once the preliminary design has been established, the detailed design phase begins. During this stage, the design of the spacecraft is refined and finalized. This involves detailed engineering of the spacecraft's systems and components, as well as extensive analysis and simulation to ensure the spacecraft's performance and reliability.
Testing
After the detailed design has been completed, the spacecraft undergoes rigorous testing. This includes environmental testing to simulate the conditions the spacecraft will encounter in space, as well as functional testing to verify the spacecraft's systems and components. The testing phase is critical to ensuring the spacecraft's readiness for launch and operation in space.
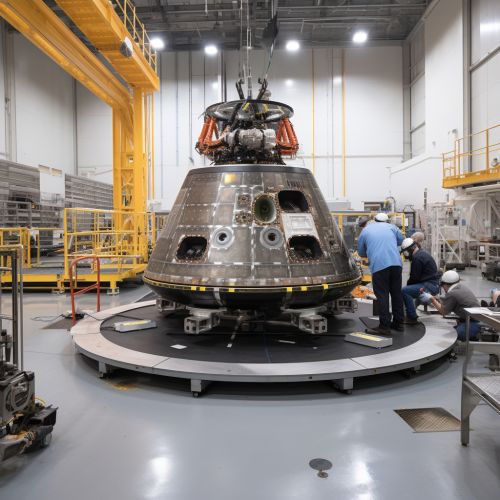


Conclusion
Spacecraft design is a complex and challenging field, requiring a deep understanding of various scientific and engineering disciplines. Despite the challenges, the field continues to advance, driven by the human desire to explore and understand the universe. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of spacecraft, opening up new possibilities for space exploration.
