Slavic languages
Introduction
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples, a branch of the Indo-European language family. This language family is the largest in Europe, with Slavic languages being spoken by nearly 315 million people.
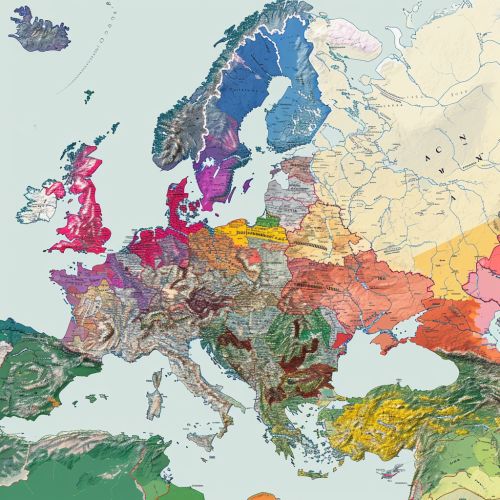
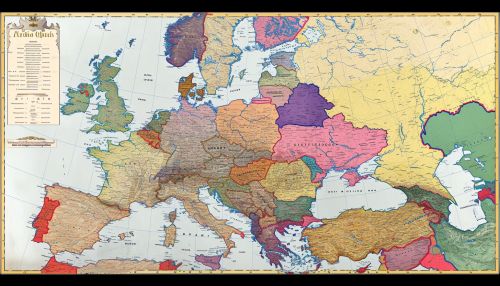
Classification
The Slavic languages are typically divided into three main branches: East, West, and South, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Each of these branches contains several languages that share common linguistic features and historical development.
East Slavic
The East Slavic branch includes Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian. These languages are primarily spoken in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus respectively, but also have significant populations of speakers in other countries.
West Slavic
The West Slavic branch includes Polish, Czech, Slovak, and the Sorbian languages. These languages are primarily spoken in Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and parts of Germany.
South Slavic
The South Slavic branch includes Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Slovenian. These languages are primarily spoken in Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Slovenia.
History
The Slavic languages, like all other Indo-European languages, have a common ancestral language, known as Proto-Slavic. This language is believed to have been spoken from the 5th to the 10th century AD.
Phonology
Slavic languages have a rich phonological system, with numerous consonant and vowel sounds. They also have a distinctive feature known as "palatalization", where the articulation of a consonant is changed by the following vowel.
Grammar
Slavic languages are highly inflected, meaning that words change form to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, gender, and number. They also have a complex system of verb aspects and a rich system of derivational morphology.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary of the Slavic languages is largely shared, with many common words across the different languages. However, each language also has its own unique words and expressions.
Writing systems
Most Slavic languages use a version of the Cyrillic or Latin alphabet. The choice of writing system often reflects historical, cultural, and political factors.
Influence and borrowings
Over the centuries, the Slavic languages have influenced and been influenced by many other languages, including Greek, Latin, German, Turkish, and English.
Modern Slavic languages
Today, the Slavic languages continue to be widely spoken and studied. They are recognized as official languages in many countries and are also significant minority languages in several others.
