Robotics
Introduction
Robotics is a branch of engineering and science that involves the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics is a rapidly growing field, as technological advances continue to create new types of robots and applications.
History
The concept of creating machines that can operate autonomously dates back to classical times, but research into the functionality and potential uses of robots did not grow substantially until the 20th century. Throughout history, it has been frequently assumed that robots will one day be able to mimic human behavior and manage tasks in a human-like fashion.
Design
The design of a robot is based on the tasks it needs to accomplish. This can range from picking up a small object, to navigating through an obstacle course, to performing complex medical procedures. The design process involves a combination of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and computer science.
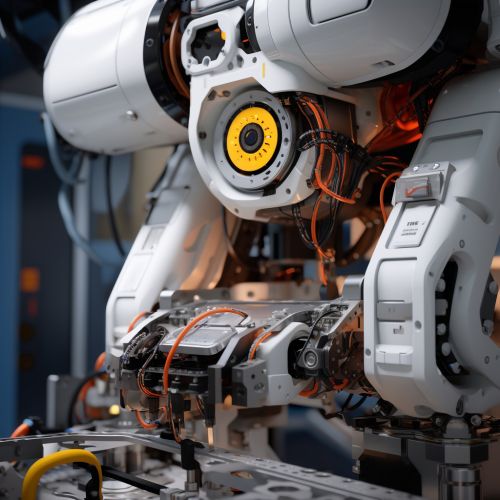
Components
Robots are typically composed of a mechanical structure, a power source, some form of system to control the robot, and systems for perception and actuation.

Control
The control of a robot involves three distinct phases – perception, processing, and action (robotic paradigms). Robots may be guided by an external control device or the control may be embedded within.
Applications
Robots are used in numerous applications, including manufacturing, healthcare, search and rescue, military, agriculture, and domestic tasks. They are also employed in some jobs which are too dirty, dangerous, or dull to be suitable for humans.
Ethics and Legal Considerations
As robots have become more advanced and sophisticated, there have been increasing debates about the social implications of robotics. Some critics of robotics argue that robots can replace humans in many jobs, leading to unemployment. Others argue that robots can free humans from mundane or dangerous tasks, allowing us to focus on more fulfilling work.
Future Trends
The future of robotics is particularly exciting, with ongoing developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as advancements in materials science and engineering that could lead to new types of robots.
