Respiratory therapy
Overview
Respiratory therapy, also known as respiratory care, is a healthcare profession dedicated to the treatment, management, control, diagnostic evaluation, and care of patients with deficiencies and abnormalities of the cardiopulmonary system. The field is closely related to pulmonology, the branch of medicine that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.
History
The profession of respiratory therapy emerged in the mid-20th century out of the increasing need for dedicated healthcare professionals to treat the growing number of patients suffering from respiratory diseases. This was largely due to the widespread prevalence of tuberculosis and polio, and the development of mechanical ventilation.
Role and Responsibilities
Respiratory therapists, also known as respiratory care practitioners, work under the medical direction of doctors and are responsible for a wide range of tasks related to patient care. These include diagnostic procedures, therapeutic treatments, and the management of patients with respiratory illnesses or conditions.
Diagnostic Procedures
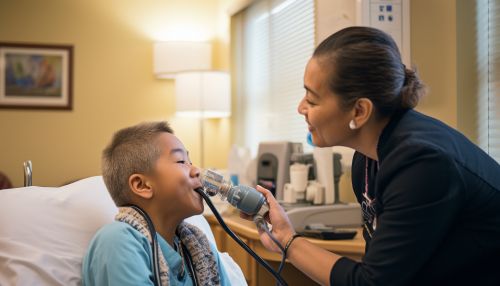
Respiratory therapists perform a variety of diagnostic tests to assess a patient's respiratory condition. These tests include pulmonary function tests (PFTs), arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, and bronchoprovocation tests. They also interpret the results of these tests to help doctors diagnose and treat respiratory diseases.
Therapeutic Treatments
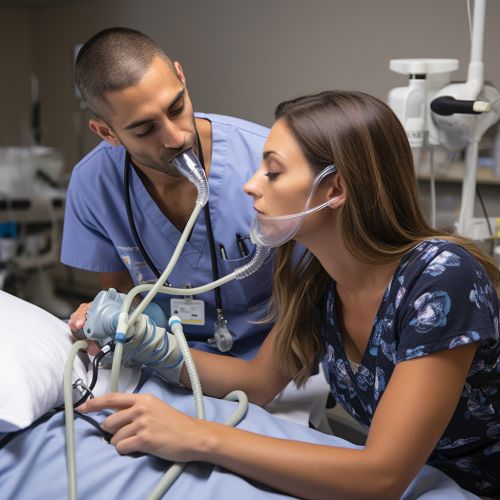
Respiratory therapists administer a wide range of therapeutic treatments to patients with respiratory conditions. These treatments include aerosol medications, chest physiotherapy, mechanical ventilation, and oxygen therapy. They also monitor and adjust the settings of life-supporting equipment, such as ventilators and artificial airway devices, to ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
Patient Management
Respiratory therapists play a crucial role in the management of patients with respiratory illnesses. They educate patients and their families about their conditions, teach them how to use medications and equipment properly, and develop care plans to manage their conditions effectively.
Education and Training
To become a respiratory therapist, individuals must complete a respiratory therapy program accredited by the Commission on Accreditation for Respiratory Care (CoARC). These programs typically lead to an associate or bachelor's degree and include coursework in anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and other related subjects.
Certification and Licensing
Upon completion of their education, prospective respiratory therapists must pass a national examination administered by the National Board for Respiratory Care (NBRC) to become certified. They must also obtain a license to practice in their state.
Future Trends
The field of respiratory therapy is expected to grow in the coming years due to the increasing prevalence of respiratory diseases, the aging population, and advances in respiratory care technology.