Quantum Information Processing
Introduction
Quantum information processing is a field of study based on the idea that information science depends on quantum effects in physics. It includes theoretical issues in computational models as well as more experimental topics in quantum physics including what can and cannot be done with quantum information. The term quantum information processing can be used to refer to quantum computation, quantum communication, quantum cryptography, and quantum teleportation.
Quantum Computation
Quantum computation uses quantum computers to perform computational tasks. Quantum computers use the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as their smallest units of information, quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits. A qubit can be in a state of 0, 1, or any superposition of these states. This allows quantum computers to perform many calculations simultaneously, potentially solving certain types of problems much more quickly than classical computers.
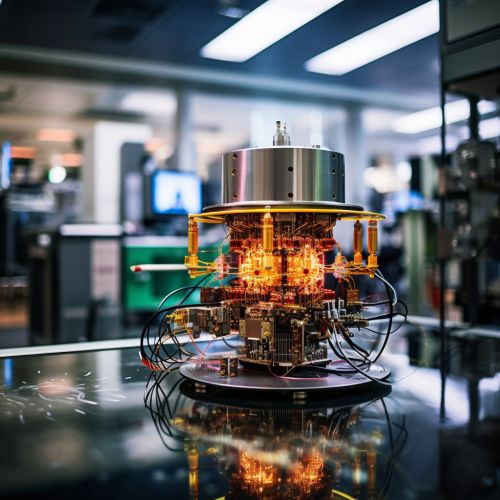
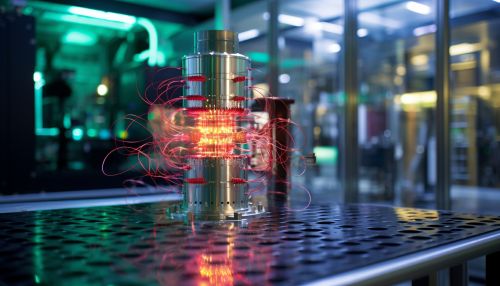
Quantum Communication
Quantum communication is a field of applied quantum physics closely related to quantum information processing and quantum teleportation. It includes the transmission of information using quantum effects, most notably quantum entanglement and quantum superposition. Quantum communication can potentially provide a level of security that is not possible with classical communication systems, as any attempt to eavesdrop on a quantum communication will inevitably disturb the quantum state of the system, alerting the communicating parties to the presence of the eavesdropper.
Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best-known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution which offers an information-theoretically secure solution to the key exchange problem. The advantage of quantum cryptography lies in the fact that it allows the completion of various cryptographic tasks that are proven or conjectured to be impossible using only classical (i.e. non-quantum) communication.
Quantum Teleportation
Quantum teleportation is a process by which quantum information (e.g. the exact state of an atom or photon) can be transmitted (exactly, in principle) from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location. It has been proven that any unknown quantum state can be teleported, assuming the two parties share an entangled pair of particles and the sender can send the receiver classical information.
Quantum Information Theory
Quantum information theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with the transmission, storage, and manipulation of quantum information. It is a result of the combination of classical information theory with quantum mechanics. Quantum information theory extends beyond the scope of classical information theory because it deals with quantum superposition states, which can hold more information than classical states.
