Quantum Imaging
Introduction
Quantum imaging is a subfield of quantum optics that exploits quantum correlations such as quantum entanglement to image objects with a resolution and image quality that is beyond what is possible in classical optics. It is a rapidly evolving field, with applications in areas such as microscopy, remote sensing, and medical imaging.
Quantum Correlations and Entanglement
Quantum correlations are a fundamental aspect of quantum physics. They arise from the quantum mechanical properties of particles, such as their wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement. Quantum entanglement, in particular, plays a crucial role in quantum imaging. When two particles are entangled, the state of one particle is directly correlated with the state of the other, no matter the distance between them. This property is used in quantum imaging to gain information about an object without directly interacting with it.

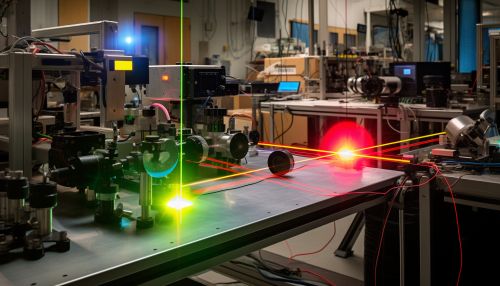
Techniques in Quantum Imaging
There are several techniques in quantum imaging, each with its own advantages and applications.
Quantum Ghost Imaging
Quantum ghost imaging is a technique that uses entangled photon pairs to image an object. One photon of the pair interacts with the object and is then detected, while the other photon, which has never interacted with the object, is also detected. The correlation between the two photons is then used to construct an image of the object.
Quantum Lithography
Quantum lithography is a technique that uses the wave nature of particles to achieve a higher resolution than classical lithography. It exploits the phenomenon of quantum interference to create patterns with a resolution that is not limited by the wavelength of the light used.
Quantum Holography
Quantum holography is a technique that uses quantum entanglement to create a holographic image of an object. The image is created by detecting the interference pattern between an object beam and a reference beam, both of which are composed of entangled photons.
Applications of Quantum Imaging
Quantum imaging techniques have a wide range of applications, from fundamental research in quantum physics to practical applications in various industries.
Microscopy
Quantum imaging can be used to improve the resolution and image quality in microscopy, allowing for the observation of structures and processes that are not visible with classical microscopy techniques.
Remote Sensing
Quantum imaging can also be used in remote sensing to gather information about an object or area from a distance. This has potential applications in areas such as environmental monitoring, military surveillance, and space exploration.
Medical Imaging
In the field of medical imaging, quantum imaging techniques could potentially be used to improve the resolution and contrast of images, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Future Directions
While quantum imaging is still a relatively new field, it holds great promise for the future. As our understanding of quantum physics continues to grow, so too will our ability to harness its potential for imaging purposes. Future research will likely focus on developing new quantum imaging techniques, improving existing ones, and exploring their potential applications.
