Pulse Jet
Introduction
A pulse jet is a type of jet engine in which combustion occurs in pulses. Pulse jets are characterized by simplicity, low cost of construction, and high noise levels. While pulse jets are not commonly used for commercial applications, they have been utilized in various military and experimental vehicles since the early 20th century.
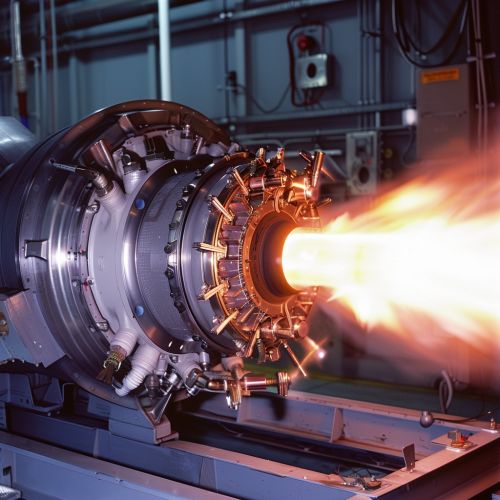

Principle of Operation
The operation of pulse jets is based on the principle of intermittent combustion, as opposed to the continuous combustion seen in most other jet engines. A pulse jet engine operates by repeating a cycle of induction, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
During the induction phase, the engine's intake valve opens to allow a mixture of fuel and air to enter the combustion chamber. This is followed by the compression phase, where the intake valve closes and the fuel-air mixture is compressed. The combustion phase begins when the compressed fuel-air mixture is ignited, creating a high-pressure pulse that propels the engine forward. Finally, the exhaust phase sees the expulsion of combustion gases from the engine, after which the cycle repeats.
Types of Pulse Jets
There are two main types of pulse jets: valved and valveless.
Valved Pulse Jets
Valved pulse jets utilize one or more valves to control the flow of fuel and air into the combustion chamber. These valves open during the induction phase to allow the fuel-air mixture to enter the chamber, and close during the compression and combustion phases to prevent the mixture from escaping. The most famous example of a valved pulse jet is the engine used in the German V-1 flying bomb during World War II.
Valveless Pulse Jets
Valveless pulse jets, on the other hand, do not use valves to control the flow of fuel and air. Instead, they rely on the engine's geometry and the momentum of the exhaust gases to draw in fresh fuel and air. Valveless pulse jets are simpler and more durable than their valved counterparts, but they are also less efficient and more difficult to start.
Applications
Pulse jets have been used in a variety of applications, ranging from military weapons to experimental vehicles.
Military Applications
The most well-known use of pulse jets was in the German V-1 flying bomb during World War II. The V-1's engine, known as the Argus As 014, was a simple valved pulse jet that produced a distinctive buzzing sound, earning the weapon the nickname "buzz bomb". Other military applications of pulse jets include target drones and decoy missiles.
Experimental Vehicles
Pulse jets have also been used in a number of experimental vehicles, including the Hiller VZ-1 Pawnee flying platform and the SNECMA Coleoptere vertical takeoff and landing aircraft. In addition, pulse jets have been used in experimental boats and cars, as well as in hobbyist projects such as model aircraft and go-karts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pulse jets offer a number of advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of jet engines.
Advantages
The primary advantage of pulse jets is their simplicity. Pulse jets have few moving parts, making them easy to construct and maintain. They are also relatively inexpensive to build, making them an attractive option for hobbyists and experimental aircraft builders. In addition, pulse jets can operate on a variety of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and even propane.
Disadvantages
The main disadvantage of pulse jets is their inefficiency. Pulse jets have a low thermal efficiency, meaning they convert a smaller percentage of their fuel's energy into useful work compared to other types of jet engines. They are also very noisy, producing a loud, buzzing sound that can be heard from miles away. Furthermore, pulse jets produce a significant amount of vibration, which can lead to structural fatigue and failure in prolonged use.
Future Prospects
Despite their limitations, pulse jets continue to be of interest for certain applications. Recent research has focused on improving the efficiency and noise levels of pulse jets through modifications to the engine's design and operation. For example, researchers are exploring the use of pulse detonation engines, a type of pulse jet that utilizes detonation waves to achieve higher efficiencies.
