Protist
Introduction
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista, which includes mostly unicellular organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms, but is not a part of the current five-kingdom system. Protists are a large group of organisms that are primarily microscopic and unicellular, or made up of a single cell.
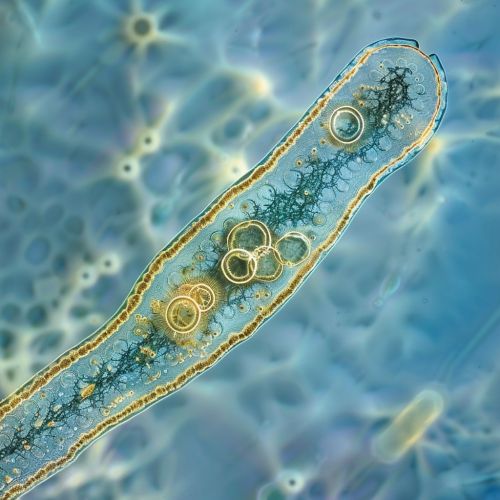
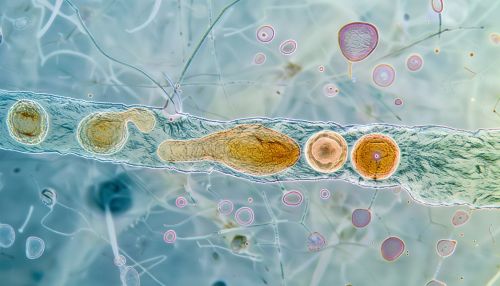
Classification
The classification of protists is still debated by scientists, and no one classification system is universally accepted. The old system of classification was the five-kingdom system, but this has been superseded by the more modern three-domain system. In the five-kingdom system, protists were grouped into a single kingdom, whereas in the three-domain system, they are spread across three different domains.
Characteristics
Protists are incredibly diverse and can have characteristics of animals, plants, or fungi. Some protists, like the amoebas, move around and take in food from their environment, much like animals. Other protists, like the euglenas, have chloroplasts and can photosynthesize, much like plants. Still, others, like the slime molds, have life cycles that resemble those of fungi.
Reproduction
Protists can reproduce in several ways, including binary fission, multiple fission, budding, and sexual reproduction. Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where the protist splits into two identical organisms. Multiple fission, also a form of asexual reproduction, involves the protist splitting into many identical organisms. Budding involves a new organism growing off the side of the original organism. Sexual reproduction in protists involves the exchange of genetic material between two protists.
Ecology
Protists play a crucial role in their ecosystems. They are often the primary producers in their food chains, converting the energy from the sun into a form that other organisms can use. Protists also play a significant role in the carbon cycle. Some protists, like the diatoms, are responsible for a significant portion of the world's oxygen production.
Human Interaction
Humans interact with protists in various ways. Some protists, like the plasmodium species that cause malaria, are harmful to humans. Other protists, like the red algae used in making sushi, are beneficial. Protists also have potential for use in biofuel production, and research is ongoing in this area.
