Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Introduction
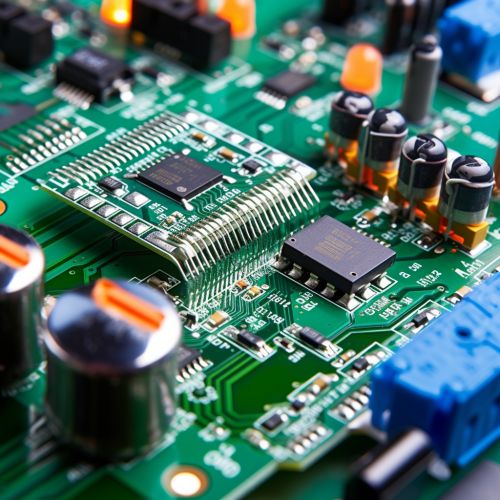
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a fundamental component in electronic devices. It mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive tracks, pads, and other features etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate.

History
The evolution of PCBs started in the early 20th century. The first patent for a "printed wire" was issued to Charles Ducas in 1925. The invention was a revolutionary step towards the development of contemporary PCBs. The printed wire was a predecessor to the printed circuit, which became widely used in the 1950s.
Design
The design of a PCB involves multiple steps and requires a deep understanding of electronic design automation (EDA) tools. The design process includes schematic capture, component placement, routing, and verification of the final design.
Manufacturing
PCB manufacturing involves several stages including board design, creating a photomask, printing, etching, drilling, plating, and finally testing for functionality. The manufacturing process is complex and requires a high degree of precision.
Types of PCBs
There are several types of PCBs, each with its own specific characteristics and applications. These include single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs.
Single-Sided PCBs
Single-sided PCBs are the simplest type of PCBs, with components and conductive patterns on one side of the board.
Double-Sided PCBs
Double-sided PCBs have conductive patterns on both sides of the board, allowing for more complex circuits.
Multi-Layer PCBs
Multi-layer PCBs consist of several layers of PCBs stacked together. They are used in high-end devices due to their ability to increase the density of the circuits without increasing the size of the board.
Applications
PCBs are used in virtually all electronic products, from simple devices like digital watches and calculators, to sophisticated systems such as computers and telecommunications equipment.
Future Trends
The future of PCBs lies in the development of flexible circuits, high-speed data, and miniaturization. The demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient devices is driving the evolution of PCB technology.
