Penicillium
Introduction
Penicillium is a genus of fungi that is of significant importance in the natural environment, food production, and health. The genus is known for its ability to produce penicillin, a compound that revolutionized the field of medicine after its discovery in 1928.
Classification and Characteristics
Penicillium belongs to the phylum Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes, and family Trichocomaceae. The genus comprises over 300 species, which are widespread in habitats where organic material is abundant. These fungi are characterized by their ability to form asexual spores, known as conidia, which are produced in chains from specialized cells called conidiophores.
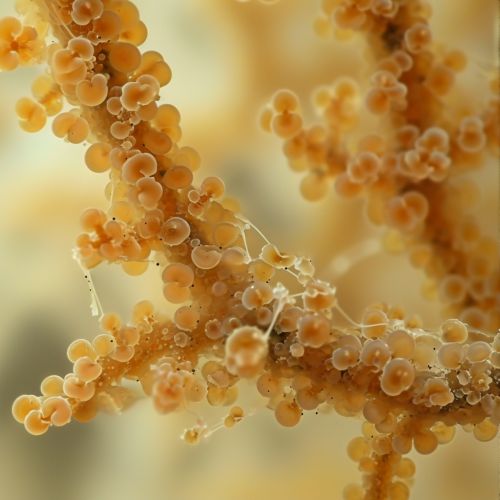
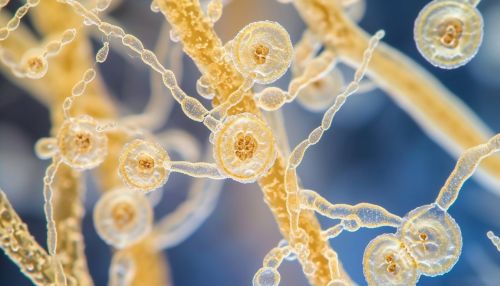
Ecology
Penicillium species are ubiquitous in nature and can be found in a variety of environments including soil, air, and decaying organic matter. They play a crucial role in the decomposition of organic materials, aiding in the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems. Some species are also known to form symbiotic relationships with plants and animals.
Economic Importance
Penicillium has a significant impact on various industries. In the food industry, certain species are used in the production of cheese, including blue cheese, Camembert, and Brie. The species Penicillium camemberti and Penicillium roqueforti are particularly important in cheese making.
In the pharmaceutical industry, Penicillium chrysogenum (formerly known as Penicillium notatum) is used for the production of penicillin, the first antibiotic to be discovered. This discovery marked a turning point in medical history, saving countless lives from bacterial infections.
Health Implications
While Penicillium is beneficial in many ways, certain species can pose health risks. Some species are known to produce mycotoxins, which can be harmful or even lethal when ingested, inhaled, or come into contact with the skin. Penicillium species are also common indoor molds and can cause health problems such as allergies and asthma in sensitive individuals.
Research and Future Prospects
Research on Penicillium continues to uncover new species and potential applications. Recent studies have identified species with potential for use in bioremediation, the use of living organisms to clean up polluted environments. Other research is exploring the potential of Penicillium species in the production of other medically important compounds.
