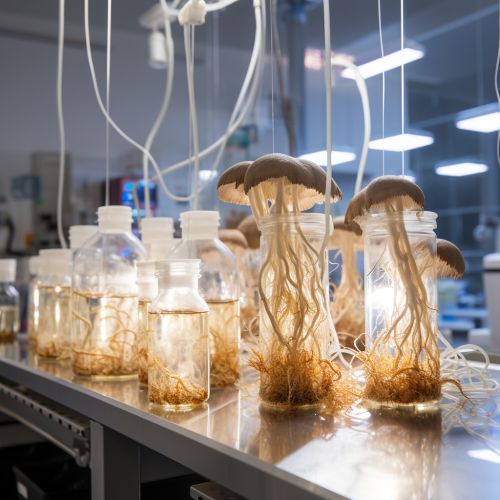
Mycelium
Introduction
Mycelium denotes the vegetative part of a fungus or fungal-like bacterial colony, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is occasionally referred to as shiro, particularly within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are prevalent in soil and on or within numerous other substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a homokaryotic mycelium, which is incapable of reproducing sexually; when two compatible homokaryotic mycelia combine and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form fruiting bodies such as mushrooms.
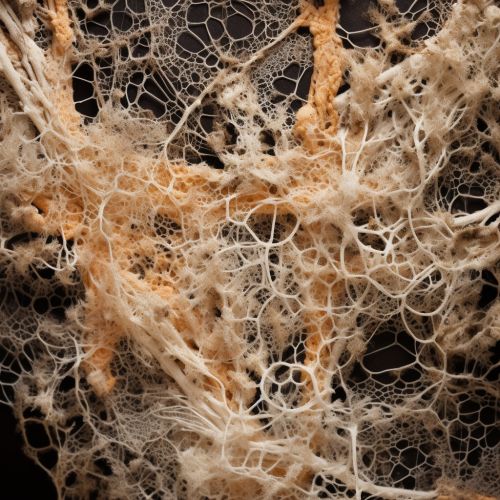

Structure and Growth
Mycelium plays a crucial role in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems due to their involvement in the decomposition of plant material. They contribute significantly to the organic fraction of soil, and their growth releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Ectomycorrhizal extramatrical mycelium, as well as the mycelium of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, enhance the efficiency of water and nutrient absorption of most plants and confer resistance to certain plant pathogens. Mycelium serves as an important food source for numerous soil invertebrates.
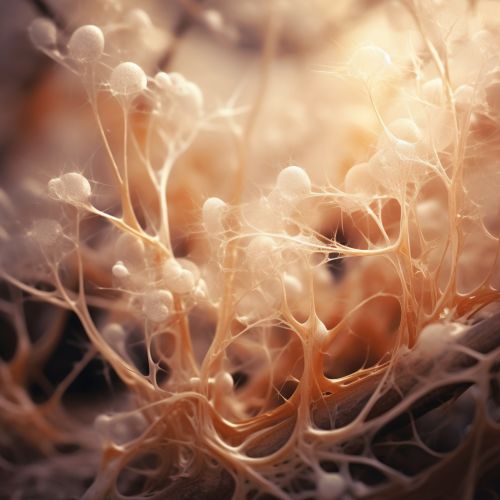

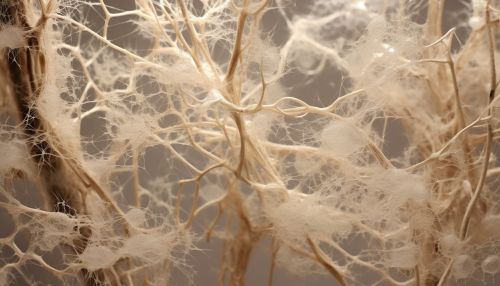
Mycelium as a Microbial Environment
Mycelium is a pivotal component in microbial communities and ecosystems. It can host a variety of bacteria and other microorganisms, providing them with a nutrient-rich environment. This symbiotic relationship can aid in breaking down complex organic materials, facilitating nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
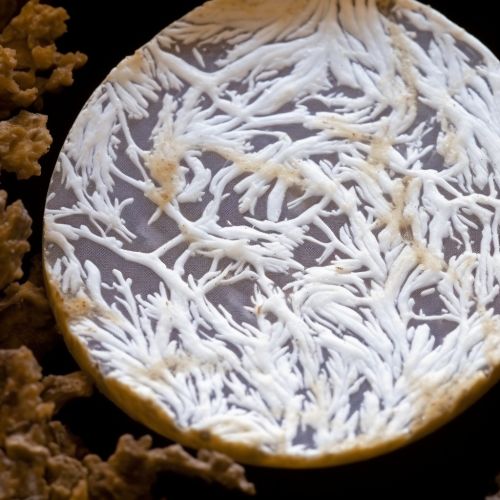

Mycelium in Industry
Mycelium holds potential uses in various industries. In the food industry, mycelium can be utilized to produce fungal biomass for use in food products. In the construction industry, mycelium can serve as a biological alternative to traditional building materials. In the textile industry, mycelium can be employed to produce a leather-like material.
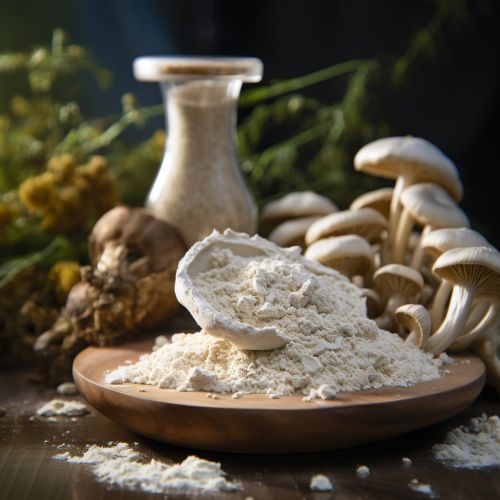


Mycelium in Medicine
Mycelium also has potential applications in medicine. Certain types of mycelium are used in the production of antibiotics, while others are being researched for their potential use in probiotics. Mycelium is also being studied for its potential use in bioremediation processes, where it can assist in breaking down toxic waste materials.


