Lunar Program
Overview
The Lunar Program is a collective term that refers to a series of missions and projects aimed at exploring the Moon, the Earth's only natural satellite. These programs have been initiated by various space agencies across the globe, with the primary objective of understanding the moon's geology, environment, and potential for human habitation.
History of Lunar Exploration
The history of lunar exploration dates back to the late 1950s, when the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union began. The first successful mission to the moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, which crash-landed on the moon's surface in 1959. This was followed by a series of Luna missions that aimed to gather data about the moon's surface and environment.
In the United States, the Apollo program was initiated by NASA in the 1960s to send humans to the moon. The program culminated in the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon.
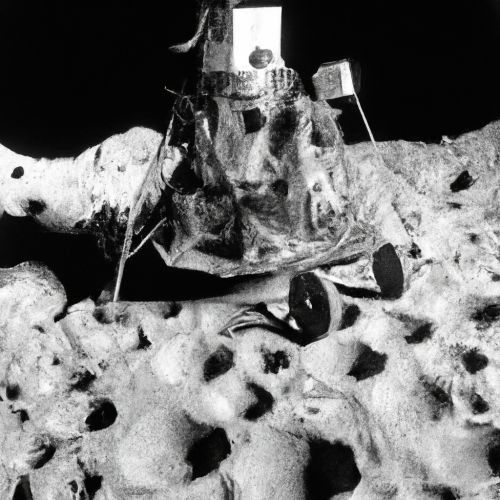
Lunar Missions
Over the years, numerous lunar missions have been launched by various countries, including the United States, Russia, China, India, and several European nations. These missions have included orbiters, landers, and rovers, each designed to carry out specific tasks and investigations on the moon.
United States
The United States has launched numerous lunar missions, most notably the Apollo program. Other significant missions include the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), which has been mapping the moon's surface since 2009, and the Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the moon by 2024.

Russia
Russia, and previously the Soviet Union, has also been actively involved in lunar exploration. The Luna program was the first to reach the moon, and subsequent missions have included orbiters, landers, and rovers. The Luna-Glob program, currently in development, aims to return lunar soil samples to Earth.
China
China's lunar program, known as the Chang'e program, has achieved several significant milestones, including the first soft landing on the far side of the moon by the Chang'e 4 mission in 2019.


India
India's lunar program, spearheaded by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), includes the successful Chandrayaan-1 mission, which discovered evidence of water on the moon, and the Chandrayaan-2 mission, which aims to land a rover on the moon's south pole.
Europe
Several European nations, under the umbrella of the European Space Agency (ESA), have also launched lunar missions. These include the SMART-1 mission, which orbited the moon from 2004 to 2006, and the planned Lunar Pathfinder mission, which aims to provide communication services for future lunar missions.
Future of Lunar Exploration
The future of lunar exploration looks promising, with several countries and private companies planning missions to the moon. These include NASA's Artemis program, Russia's Luna-Glob program, China's Chang'e program, and India's Chandrayaan program. In addition, private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are developing technologies to facilitate lunar exploration and potential human habitation.


