Laparoscopy
Overview
Laparoscopy is a type of surgical procedure that allows a surgeon to access the inside of the abdomen (tummy) and pelvis without having to make large incisions in the skin. This procedure is also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery. Large incisions can be avoided during laparoscopy because the surgeon uses an instrument called a laparoscope.
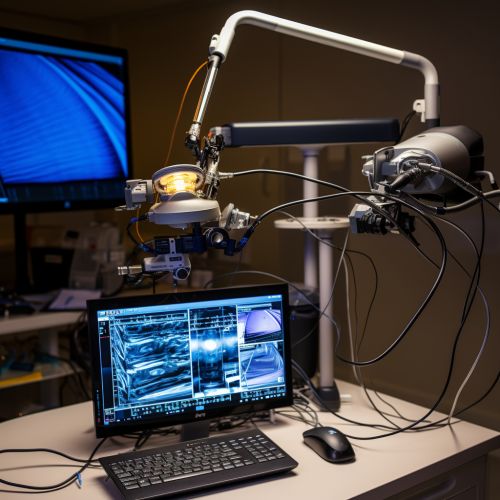

Procedure
During a laparoscopy, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions in the abdomen. These allow the surgeon to insert the laparoscope, a small tube that has a light source and a camera, which relays images of the inside of the abdomen or pelvis to a television monitor. The advantages of this technique over traditional open surgery include a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery time; less pain and bleeding after the operation; and reduced scarring.
Uses
Laparoscopy can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions that can affect the organs inside the abdomen or the female pelvic organs. Laparoscopy is often used to identify the source of abdominal pain or a lump. It can also be used for female reproductive problems such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, or female infertility.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications with laparoscopy. These include infection, bleeding, damage to organs, and complications related to the anesthesia. However, serious complications are rare.
Recovery
After a laparoscopy, you'll be moved to a recovery room to allow the effects of the anesthesia to wear off. You may feel a little sore around the cuts, but this is normal. You should be able to go home the same day or the day after. You'll need to arrange for someone to take you home as you won't be able to drive for a while.
