History of dyes and pigments
Early History
The history of dyes and pigments is as old as the human civilization itself. The earliest evidence of the use of dyes dates back to the Neolithic era, around 10,000 BC, where early humans used natural substances to color animal skins, bones, and other materials. These early dyes were derived from plants, animals, and minerals, and were used not only for aesthetic purposes but also for symbolic and ritualistic ones.


Natural Dyes
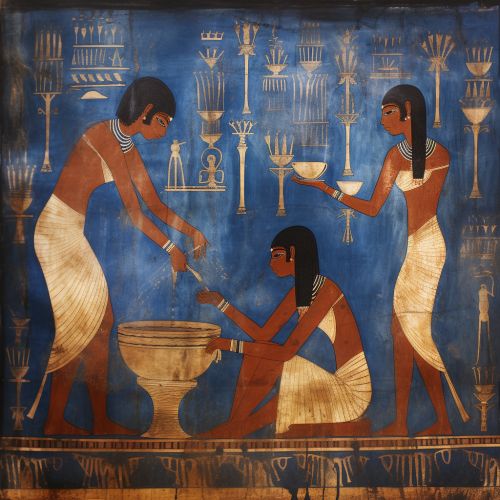
The use of natural dyes continued to evolve and expand throughout the ancient world. The Egyptians, for example, were known for their use of indigo, a plant-based dye that produces a deep blue color. They also used other natural dyes such as henna for body art and turmeric for textile coloring.
In ancient Rome and Greece, the most prized dye was Tyrian purple, a color so difficult to produce that it became a symbol of power and wealth. This dye was extracted from the murex sea snail and required thousands of snails to produce just a small amount of dye.

Development of Synthetic Dyes
The 19th century marked a significant turning point in the history of dyes and pigments with the development of synthetic dyes. In 1856, an 18-year-old British chemist named William Henry Perkin accidentally discovered the first synthetic dye, known as mauveine or simply mauve, while attempting to synthesize quinine, a treatment for malaria. This discovery revolutionized the dye industry, leading to the production of a wide range of synthetic dyes with a variety of colors and properties.


Modern Dyes and Pigments
Today, the majority of dyes and pigments used are synthetic. These modern dyes and pigments are used in a wide range of industries, from textiles and plastics to food and cosmetics. They are also used in scientific research, particularly in the field of fluorescence microscopy, where fluorescent dyes are used to stain cells and tissues for observation under a microscope.


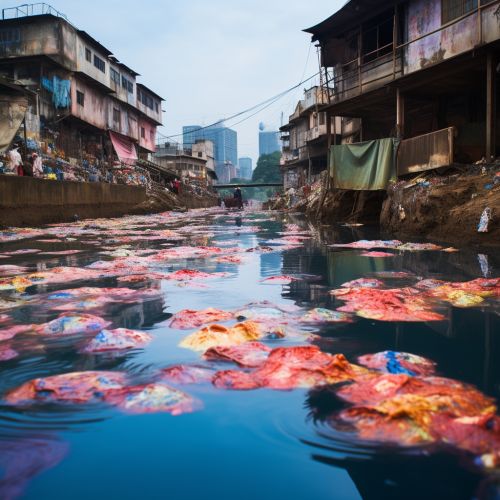
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The production and use of dyes and pigments have significant environmental implications. Many synthetic dyes are toxic and can cause environmental pollution if not properly managed. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the development of sustainable and environmentally friendly dyes and pigments. This includes the use of natural dyes, the development of biodegradable synthetic dyes, and the implementation of cleaner production processes.


