Computer-Aided Design
Introduction
Computer-aided design (CAD) is a technology that uses computer systems to assist in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. CAD software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations.
History
The development of CAD software has a long history. The birth of CAD can be traced back to the 1960s when Dr. Patrick J. Hanratty developed PRONTO (Program for Numerical Tooling Operations), the first commercial numerical-control programming system. In 1971, the first version of AutoCAD was released, which is still one of the most widely used CAD software today.
Types of CAD Software
There are several types of CAD software available, each with its unique features and uses. These include 2D CAD, 3D CAD, 3D Wireframe and Surface Modelling, and Solid Modelling.
2D CAD
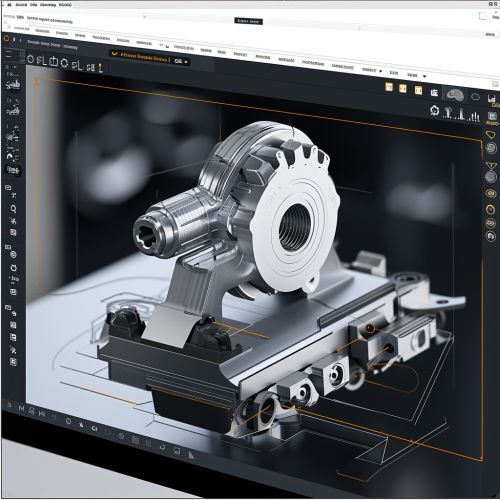
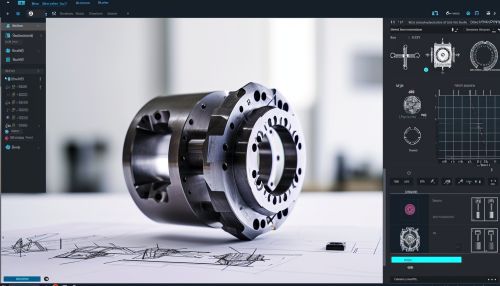
2D CAD is primarily used for creating flat drawings of products and structures. It is often used by architects, civil engineers, and other professionals who need to create blueprints and floor plans.
3D CAD
3D CAD, also known as solid modeling, is used to create a realistic model of a physical object. This type of CAD software allows designers to visualize the final product, perform simulations, and conduct analyses on the design.
3D Wireframe and Surface Modelling
3D Wireframe and Surface Modelling is a more complex form of CAD design. It involves creating a skeletal three-dimensional model in which all the surfaces are visibly open. The model is created by specifying each edge of the physical component in two or three dimensions.
Solid Modelling
Solid Modelling is the most comprehensive type of CAD and is often used in engineering and manufacturing. It creates a complete, three-dimensional representation of a design, including its internal components.
Applications of CAD
CAD software is used in many industries, including automotive, aerospace, industrial design, architecture, and many others. It is used to design everything from cars to skyscrapers to consumer products.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, CAD is used to design and test vehicles. Engineers can create a virtual model of a car, allowing them to test various aspects such as aerodynamics, crash resistance, and fuel efficiency without having to build a physical prototype.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, CAD is used to design aircraft and spacecraft. It allows engineers to create 3D models of aircraft parts, simulate flight conditions, and analyze the performance of the design.
Industrial Design
In industrial design, CAD is used to create designs for a wide range of consumer products, from furniture to electronics. Designers can create a 3D model of the product, allowing them to visualize the final product and make any necessary adjustments before it goes into production.
Architecture
In architecture, CAD is used to create 3D models of buildings and structures. It allows architects to visualize the final structure, conduct simulations, and make any necessary adjustments before construction begins.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CAD
Like any technology, CAD has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
One of the main advantages of CAD is that it allows for easy design modifications. With traditional hand-drawn designs, any changes would require the entire design to be redrawn. With CAD, however, changes can be made easily and quickly.
Another advantage is that CAD allows for more accurate designs. CAD software can be programmed to follow specific design standards, ensuring that the final design is accurate and meets all necessary specifications.
Finally, CAD allows for easier collaboration. Multiple designers can work on the same design simultaneously, and the design can be easily shared with others.
Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of CAD is the cost. CAD software can be expensive, and there is also the cost of training staff to use the software.
Another disadvantage is that CAD can be time-consuming. While it can speed up the design process in some cases, in others it can take longer to create a design using CAD than it would by hand.
Finally, there is the risk of over-reliance on CAD. While CAD can be a valuable tool, it is important to remember that it is just that – a tool. It should not replace the skills and knowledge of the designer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CAD is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the design process in many industries. While it has its disadvantages, the benefits it offers in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration make it an invaluable tool for designers.
