Clay Nanoparticles
Introduction
Clay nanoparticles are a class of nanomaterials that are derived from clay minerals. These particles have at least one dimension in the nanometer range (1-100 nm), which gives them unique properties compared to their bulk counterparts. Clay nanoparticles have been extensively studied for their potential applications in various fields such as material science, environmental science, medicine, and energy storage.
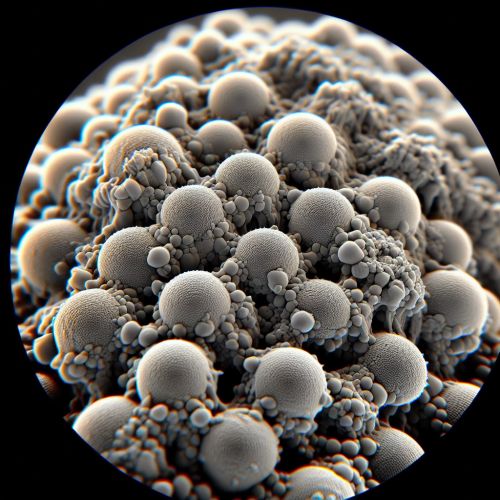
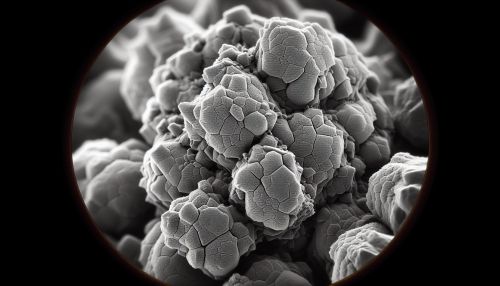
Structure and Properties
Clay nanoparticles are typically composed of layered silicate minerals. The most common types of clay nanoparticles are montmorillonite, kaolinite, halloysite, and bentonite. These nanoparticles have a layered structure, with each layer consisting of one alumina sheet sandwiched between two silica sheets. The layers are held together by van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds.
The small size and high surface area of clay nanoparticles give them unique physical and chemical properties. For example, they have excellent thermal stability, high mechanical strength, and good adsorption capacity. Furthermore, the interlayer space in clay nanoparticles can be modified to incorporate various functional groups, which can enhance their reactivity and compatibility with other materials.
Synthesis Methods
There are several methods for synthesizing clay nanoparticles, including mechanical exfoliation, chemical exfoliation, and ion-exchange methods. Mechanical exfoliation involves the use of shear forces to separate the layers of clay minerals. Chemical exfoliation involves the use of chemicals to break the bonds between the layers. Ion-exchange methods involve the replacement of interlayer cations with other cations, which can cause the layers to separate.
Applications
Due to their unique properties, clay nanoparticles have a wide range of applications. In material science, they are used to enhance the properties of polymer nanocomposites. For example, they can improve the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and barrier properties of polymers. In environmental science, they are used for the removal of pollutants from water and soil due to their high adsorption capacity. In medicine, they are used for drug delivery, wound healing, and tissue engineering. In energy storage, they are used as electrode materials for supercapacitors and batteries.
Future Perspectives
The field of clay nanoparticles is still in its early stages, and there is much potential for future research and development. One area of interest is the design and synthesis of functionalized clay nanoparticles with enhanced properties. Another area of interest is the development of novel applications for clay nanoparticles in fields such as electronics, photonics, and biotechnology.
