Cell junction
Introduction
A cell junction is a type of structure found in all cells that allows them to connect with each other. These junctions play crucial roles in communication between cells, maintaining tissue structure, and enabling cells to function as a coordinated unit in multicellular organisms.
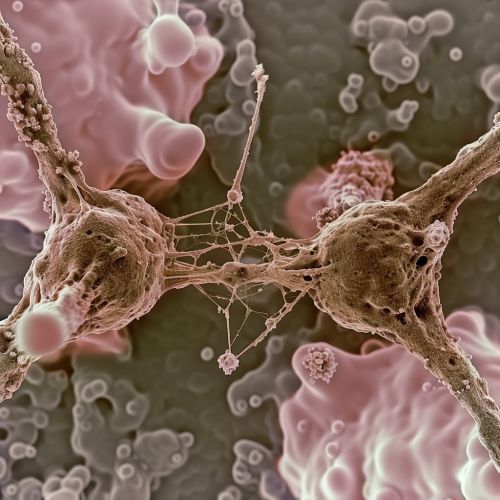
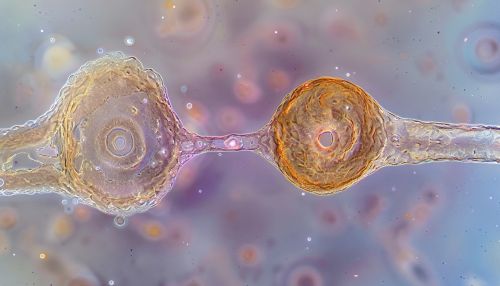
Types of Cell Junctions
There are three primary types of cell junctions: tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions. Each type has a unique structure and function, and they often work together to ensure the integrity and functionality of tissues.
Tight Junctions
Tight junctions are a type of cell junction that forms a barrier between cells. They are located at the apical end of the lateral membrane and create a seal that prevents the passage of substances between cells. This seal is crucial in maintaining the polarity of cells, which is essential for the proper functioning of epithelial tissues.
Adherens Junctions
Adherens junctions are cell junctions that connect the actin filament bundle in one cell with that in the neighbor cell. They play a key role in connecting cells within tissues and are particularly important in maintaining tissue structure during changes in cell shape and cell movement.
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are a type of cell junction that allows for communication between cells. They are composed of protein channels that create a direct pathway for small molecules and ions to pass from one cell to another. This communication is crucial for many physiological processes, including cell growth and differentiation, tissue development, and the coordination of cellular activities.
Structure and Composition of Cell Junctions
Cell junctions are complex structures composed of various proteins that interact with each other to form a functional unit. The specific composition of a cell junction depends on its type and function.
Tight Junction Structure and Composition
Tight junctions are composed of a network of sealing strands, each strand acting as a barrier to prevent the movement of substances between cells. The primary components of these strands are proteins called claudins and occludins. These proteins interact with each other and with other proteins to form the tight junction structure.
Adherens Junction Structure and Composition
Adherens junctions are composed of cadherin proteins that interact with each other to form a strong adhesive bond between cells. These cadherins are connected to the actin cytoskeleton within the cell, providing a structural link between cells.
Gap Junction Structure and Composition
Gap junctions are composed of two connexons, one each from the adjoining cells. Each connexon is a hexamer of proteins called connexins. These connexins form a pore that allows for the passage of small molecules and ions between cells.
Function of Cell Junctions
Cell junctions play a variety of roles in maintaining the structure and function of tissues. They are involved in cell adhesion, communication between cells, and the establishment of cell polarity.
Function of Tight Junctions
Tight junctions play a crucial role in maintaining the polarity of cells by preventing the movement of proteins and lipids between the apical and basolateral domains of the cell membrane. They also form a barrier that prevents the passage of substances between cells, thereby controlling the movement of substances through the paracellular pathway.
Function of Adherens Junctions
Adherens junctions play a key role in maintaining tissue structure by connecting cells within tissues. They are particularly important during changes in cell shape and cell movement, as they provide a structural link that allows cells to move as a coordinated unit.
Function of Gap Junctions
Gap junctions play a crucial role in communication between cells. They allow for the direct passage of small molecules and ions between cells, enabling cells to coordinate their activities. This communication is essential for many physiological processes, including cell growth and differentiation, tissue development, and the coordination of cellular activities.
Conclusion
Cell junctions are complex structures that play crucial roles in maintaining the structure and function of tissues. They are involved in cell adhesion, communication between cells, and the establishment of cell polarity. Understanding the structure and function of cell junctions is essential for understanding the biology of multicellular organisms.
