Betacoronavirus
Introduction
Betacoronavirus is a genus of the Coronaviridae family of viruses, within the order Nidovirales. This genus is comprised of several species of viruses that can cause illness in mammals, including humans.

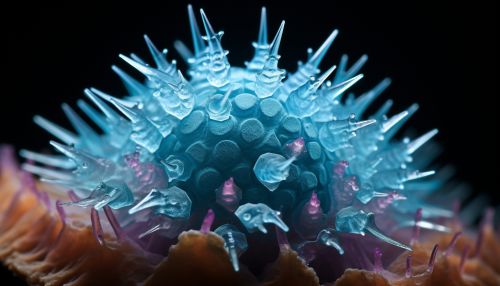
Taxonomy
The Betacoronavirus genus is divided into five subgenera: Embecovirus, Sarbecovirus, Merbecovirus, Nobecovirus, and Hibecovirus. Each subgenus contains multiple species of viruses, with the most well-known being the SARS-CoV-2, which is responsible for the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Structure
Betacoronaviruses are enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses. They are characterized by club-like spikes that project from their surface, an unusually large RNA genome, and a unique replication strategy.
Pathogenesis
Betacoronaviruses are known to cause respiratory, enteric, hepatic, and neurological diseases of varying severity in animals and humans. The severity of the diseases can range from mild to severe, and can sometimes lead to death.
Transmission
Betacoronaviruses are primarily transmitted through direct contact with secretions of an infected person or animal, or by touching surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touching the face.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention measures for Betacoronavirus infections are similar to those for other respiratory viruses and include hand hygiene, wearing masks, and social distancing. Treatment is largely supportive, with care aimed at relieving symptoms and maintaining bodily functions.
