Azotobacter beijerinckii
Introduction
Azotobacter beijerinckii is a species of free-living, aerobic, nitrogen-fixing bacteria that belongs to the genus Azotobacter. The genus Azotobacter is known for its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form that can be utilized by plants. This species is named after Martinus Beijerinck, a Dutch microbiologist who made significant contributions to the field of microbiology, including the discovery of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
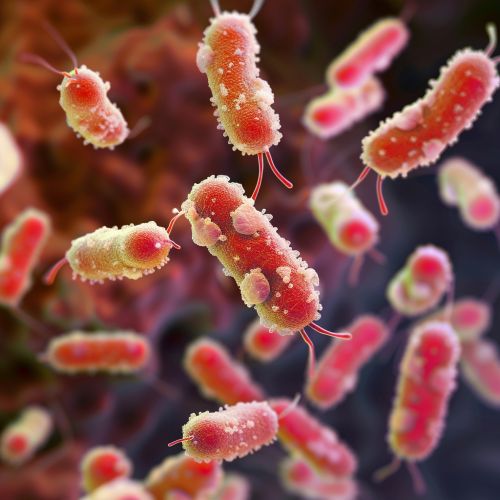
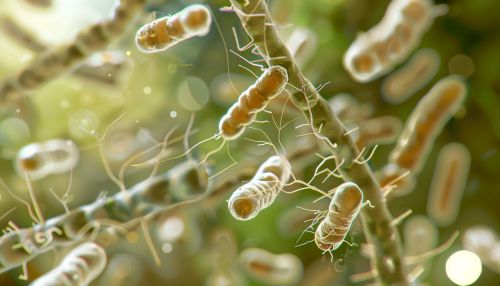
Taxonomy and Classification
Azotobacter beijerinckii falls under the family Azotobacteraceae, order Pseudomonadales, class Gammaproteobacteria, phylum Proteobacteria, and domain Bacteria. It is one of the six species of the genus Azotobacter, which are all known for their nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
Morphology and Structure
Azotobacter beijerinckii is a rod-shaped bacterium with a size of approximately 2-5 micrometers in length and 1-2 micrometers in width. The cells are often found in pairs or chains. They are gram-negative, which means they do not retain the violet crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method. Instead, they take up the red counterstain used in the procedure, giving them a pink or red appearance under the microscope.
Metabolism and Nitrogen Fixation
Azotobacter beijerinckii, like other species in the Azotobacter genus, is capable of atmospheric nitrogen fixation. This process involves the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3), a form that can be used by plants. This process is facilitated by the enzyme nitrogenase, which is highly sensitive to oxygen. To protect this enzyme, Azotobacter produces a protective layer of slime, or exopolysaccharide, around the cells.
Ecological Role and Significance
Azotobacter beijerinckii plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle, one of the most important nutrient cycles in terrestrial ecosystems. By converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by plants, it helps to replenish the soil's nitrogen content, promoting plant growth and productivity. This is particularly important in agricultural systems, where nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient.
Industrial Applications
Due to its nitrogen-fixing capabilities, Azotobacter beijerinckii has potential applications in agriculture as a biofertilizer. It can be used to enrich the soil with nitrogen, reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers. Additionally, the exopolysaccharide produced by Azotobacter beijerinckii has potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries as a thickening agent or stabilizer.
